Maths is a broad subject, covering addition and subtraction, division, fractions, graphs, rounding, solving equations, algebra, inequalities, variables, statistics, substitution, trig, computation, distributive property, symmetry, whole numbers, prime numbers, probability, value, vectors, shapes, sequence, proportion, and more! That is why mathematics is always around us, everywhere we go.
Before diving deeper into the history and impact of these formulas, here’s a quick list of the 10 famous mathematical equations covered in this article—each a pillar of scientific and mathematical thought:
- Pythagoras' Theorem: A fundamental rule in geometry that relates the sides of a right-angled triangle—one of the most important formulas in math.
- Logarithms: Simplify complex calculations and laid the foundation for the slide rule, helping scientists in the pre-digital age.
- The Law of Gravity: Newton’s formula that describes the force of attraction between two masses—one of the 17 equations that changed the world.
- The Theory of Relativity: Einstein’s groundbreaking insight showing that mass and energy are interchangeable, revolutionizing modern physics.
- Chaos Theory: A nonlinear equation showing how tiny changes in input can lead to wildly different outcomes—key to understanding unpredictable systems.
- Euler's Identity: Often called the most beautiful equation in math, it unifies five fundamental mathematical constants.
- The Fourier Transform: Converts signals from the time domain to the frequency domain, essential in engineering, image processing, and quantum physics.
- Maxwell's Equations: Four formulas that describe how electric and magnetic fields interact—paving the way for wireless communication and modern electronics.
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics: States that entropy in a closed system always increases—central to understanding energy, heat, and the direction of time.
- The Schrödinger Equation: A key result in quantum mechanics that describes how particles behave at atomic and subatomic levels.
These are not just famous math formulas, but among the most important formulas in math, physics, and engineering—contributing to everything from how we build bridges to how we understand the universe.
Find your online maths tutor on Superprof and learn basic Maths concepts from a certified Maths teacher in your area.
Complex equations with many unknowns, as well as radical mathematical theorems dating back to antiquity and late twentieth-century discoveries, have all shaped our world.

Who Invented Math Formulas?
It's difficult to say who exactly "invented" mathematical formulas, as mathematics is a field that has evolved over thousands of years, with contributions from many different cultures and civilizations.
Mathematics, as we know it today, has its roots in ancient civilizations such as the Babylonians, Egyptians, and Greeks. These civilizations developed mathematical concepts, algorithms, and formulas to solve practical problems related to trade, commerce, and engineering.
For example, the ancient Greeks developed the concept of geometry and theorems such as Pythagoras' theorem, while the Babylonians developed methods for solving linear and quadratic equations.
Father of Mathematics
The title of "Father of Mathematics" is often given to the ancient Greek mathematician Pythagoras. Pythagoras was a philosopher, mathematician, and founder of the Pythagorean School of Mathematics in ancient Greece. He is credited with many contributions to the field of mathematics, including the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
How Old are Maths Formulas?
Since maths is a broad application of matter, rather than a discovery, we cannot credit one person with the invention of maths itself (unless you want to be really deep and say that the creator of our universe is responsible for the birth of maths!). However, we can take a look back at when maths started to play a role in the life of humans.
Unsurprisingly, evidence shows that even those living in prehistoric times had some understanding of maths concepts, records of which were found on many items, like bones, and wall carvings.
Markings would have shown that they used rational thinking when learning how to solve simple math problems like adding things up on a surface area. So what would have driven them to take an interest in mathematics in the first place? The passing of time, for instance, would have intrigued them. Working out how long they had left to hunt for food before sunset, maybe, which they would have looked at astronomy to answer.
The Star Garden states that:
"The Ishango bone is about 20,000 years old and has a series of notches carved into it in three columns. Patterns in these numbers may show that they were made by someone who understood addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and prime numbers."
They go on to say that:
"People understood geometry and algebra by about 2000 BCE [...] Around this time, both the Babylonians and Ancient Egyptians were aware of the number ? (pi) the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. By about 1500 BCE, the Babylonians were also aware of Pythagoras' theorem, which shows how the lengths of the sides of right-angled triangles are related."
The theorem is named after ancient Greek mathematician Pythagoras (though some say the concept predates him) which shows that, although all maths theorems and formulae simply exist and are waiting to be discovered, we can at least praise some individuals for find them or working them out.
In their brief history of Maths, The Star Garden website adds that: "Kepler was also inspired by Pythagoras, and believed that the motion of the planets produces music. He used mathematics to show that the planets orbit the Sun in ellipses and, by 1619, he was able to determine the time it takes each planet to orbit and their relative distances from the Sun.
In 1687, Newton published his law of universal gravitation. This was groundbreaking because it showed, not just that abstract mathematical principles, such as the newly invented calculus, could be applied to what we observe in nature, but that the laws responsible for the movement of the planets are also responsible for the movement of objects on Earth. Newton also believed that the universe could be understood as a mathematical object, and described God as "skilled in mechanics and geometry".
Newton's contemporary, Leibniz, discovered another link between mathematics and nature when he first considered the idea of fractals. [...] Twentieth-century mathematicians, such as French mathematician Gaston Julia and Polish-French-American mathematician Benoit Mandelbrot, were inspired by Leibniz to create complicated fractals of their own.
By this time, quantum mechanics, and German-Swiss-American physicist Albert Einstein's theories of special and general relativity, had shown that nature obeys the laws of mathematics, even when this contradicts our common sense understanding of the world."
So, as we can see, Maths has been ever-present throughout the history of Man, yet a number of significant breakthroughs have emerged thanks to skilled mathematicians who have come to find them. We will look at some of the most famous maths equations below.
As a final note on the history of maths, it is important to note that, despite humans not developing with the use of mathematical concepts, maths has always played a part on the planet. Even before the existence of people, maths would have dictated all nature, plus the energy sources and animals that graced Earth, thanks to its necessity in reproduction and life in general.
10 Famous Maths Equations
If you wonder why maths is so important, and the impact that each major equation has wrought, read on to discover 10 revolutionary formulas to take your maths tuition to another level. There is, of course, no end to the number of mathematical formulas and expressions that exist (some might say the list is infinite!), but here we focus on some of the better known algebraic equation and prvide some helpful notation.
Don't forget, Superprof can help you find the perfect math tutor if you become inspired to get math help using a math teacher or online math help!
Pythagoras' Theorem
This is surely one of the best-known theorems. Even years after your last maths class, its name springs easily to mind.
You may know it by heart, but let's quickly recap: In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the square roots of the lengths of the other two sides.
This theorem, which dates back to 530 BCE, is one of the foundations of maths to this day, and has contributed to the history of maths ever since its discovery.
This equation is essential to an understanding of geometry and trigonometry, and indeed has shaped our understanding of those branches of mathematics.
It is said that we have moved from Euclidean geometry to non-Euclidean geometry.
Since then, thanks to Pythagoras and his famous equation, it's now easy to calculate lengths, angles and to demonstrate that a given triangle is right-angled.
This concept is often to be found in the realms of construction and architecture.
Logarithms
Logarithms, popularised by John Napier in 1610, combine inverse and exponential functions, and opposites.
Logarithms are common in formulas used in science, to measure the complexity of algorithms and fractals, and appear in formulas for counting prime numbers.
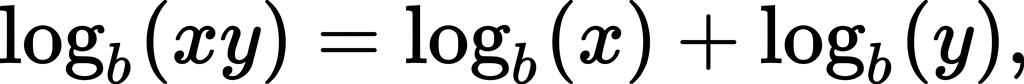
Until the development of the modern computer, calculating with logarithms was the most usual way of multiplying large numbers together, and made possible faster calculations, but above all helped make leaps and bounds in the fields of maths, physics, engineering and astronomy.
There are 3 types of logarithm:
- Natural logarithms are the fundamental basis in mathematical analysis
- Decimal logarithms are used in mathematical calculations
- Binary logarithms are used in computational theory and for applied calculations
The logarithm of a number is the exponent to which another fixed number, the base, must be raised to produce that number.
For example, in the case of base 10, the logarithm (log) is: Log (1) = 0, log (10) = 1, log (100) = 2.
Such calculations are useful in, for example, poker, and in solving puzzles.
The Law of Gravity
Who has never heard of Isaac Newton's famous law of gravity? You know the story of the apple which fell on the great thinker's head while he pondered the moon in the night sky, in the year 1687.
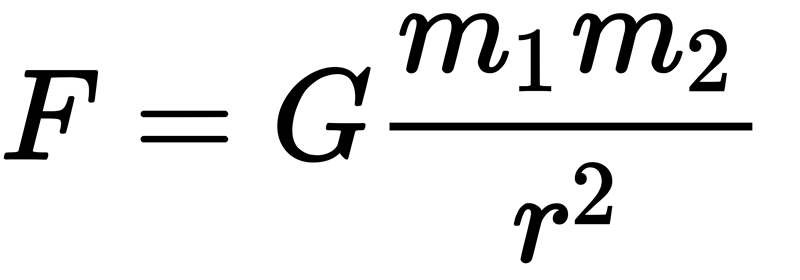
It was by drawing a connection between these two bodies (the moon and the apple) that Newton then wondered: Why does the moon not fall from the sky?
The answer is obvious - now: It is "held up" by a gravitational force.
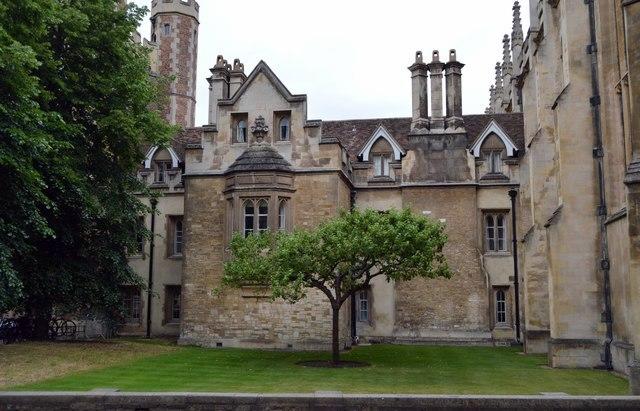

Thus was born Newton's famous law of gravity: "Astral bodies attract each other with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centres."
200 years after Newton, Einstein replaced this theory of gravitation by his theory of relativity.
Discover maths tutors near me and get help learning advanced concepts on Superprof.

The Theory of Relativity
Whether one is versed in mathematics or physics, or knows nothing of the vocabulary of maths, everyone knows Albert Einstein's famous formula: E = mc².
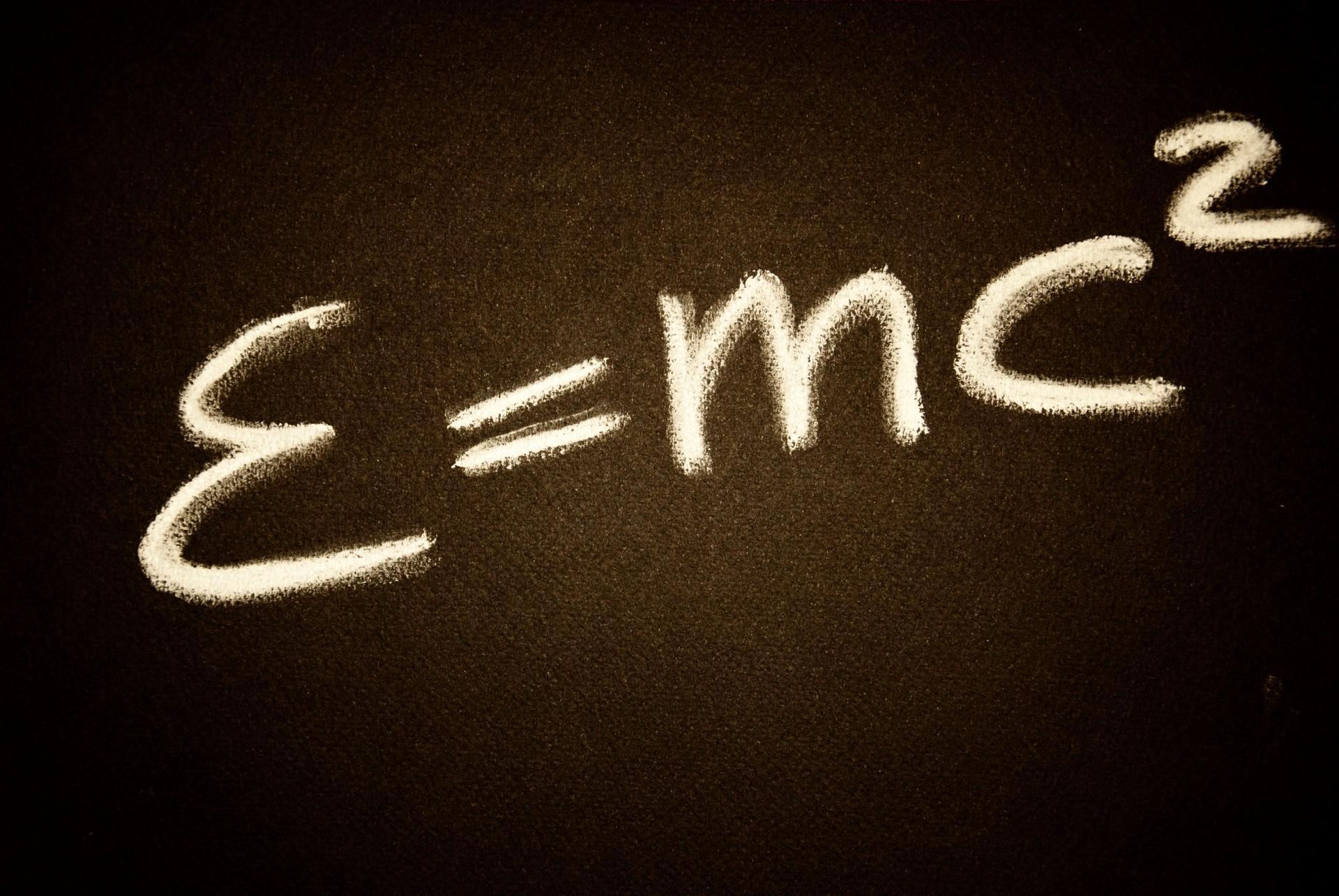
This formula, which illustrates the theory of relativity (restricted relativity and general relativity) revolutionised our understanding of physics up to that point.
It remains crucial to this day, as it shows that matter can be converted into energy and vice versa.
Restricted relativity introduced the idea that the speed of light was a universal constant that did not change, and that the passage of time was not the same for bodies moving at different speeds.
Einstein's general relativity describes the gravity in which space and time are curved and folded: A major change in our understanding following Newton's law of gravity.
Even today, Einstein's theory of relativity remains essential in our understanding of the origin, structure and destiny of our Universe.
Maths helps us better understand the world around us, and is an omnipresent force in our daily lives.
Chaos Theory
Chaos theory has shown us that it's impossible to predict with certainty what will happen in the future. It is the study of the behaviour of dynamic systems. A great topic to learn maths.
This theory proves that no really existing processes may be predicted with certainty. Robert May's theory is more recent, dating from 1975. It describes a process that is constantly evolving over time.
In his formula, May wanted to explain that chaotic behaviour (like climate, which experiences numerous changes in weather from moment to moment) can lead to changes in other completely different systems a few days later.
The best-known illustration is the so-called "butterfly effect" which shows that the beating of a butterfly's wings in Brazil can lead to a hurricane or tornado in Asia.
In other words, the most insignificant of things can have unsuspected effects on our environment, near and far.

It is the multiplicity of factors related to an event that makes it unpredictable.
Euler's Identity
Euler's identity is considered to be "the finest of equations" in maths classes because it describes an unlikely combination of five mathematical constants.
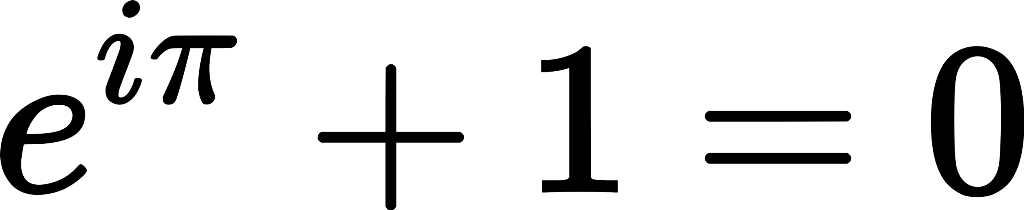
Euler's equation (published by Leonhard Euler in 1755) applies in the case of a perfect fluid.
Why does this equation matter? Because it makes use of three fundamental operations in arithmetic: addition, multiplication and exponentiation.
The five constants represented are "0", the additive identity; "1", the multiplicative identity; the fabulous pi; "e" which is the base of natural logarithms and a number which widely occurs in mathematical analyses; and "i", the imaginary unit of the complex numbers found in equations with 3 unknowns.
This equation, which decorates the Palais de la Découverte in Paris, paved the way for the development of topology, a branch of modern maths.
The Fourier Transform
The Fourier transform divides time into several frequencies and simple waves, just as a prism splits light in its constituent colours.
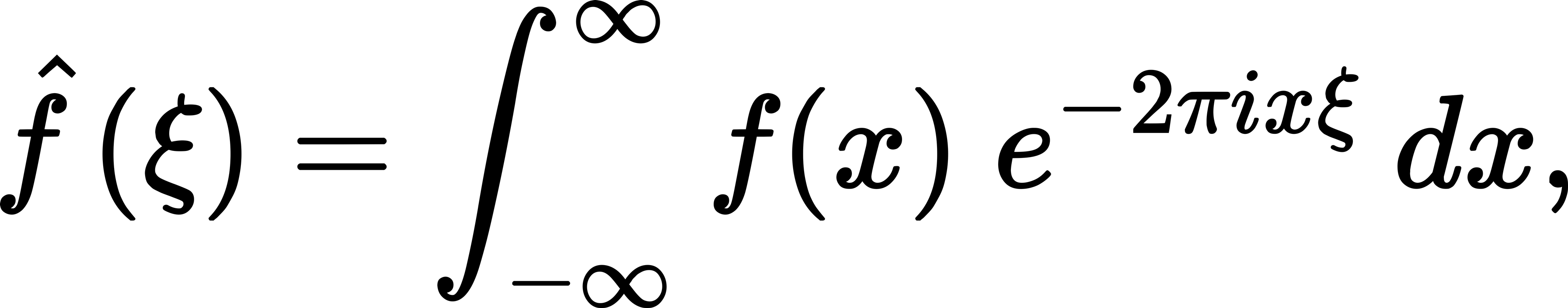
The Fourier transform allows us to deal with non-periodic functions.
Another example could be a magnetic or an acoustic field that is defined as a signal. The Fourier transform is its spectrum, in that it deconstructs such a field.

This theory was so earth-shaking because, suddenly, it was possible to understand the structure of more complex waves, such as human speech.
Today this theory, which dates back to 1822, goes to the heart of modern signal processing and analysis, as well as data processing.
Get help learning everything you need to know when you find maths tutors near me on Superprof.
Maxwell's Equations
Maxwell's equations describe how electric charges interact, as well as explaining electric currents and magnetic fields.
Maxwell's equations, also called Maxwell-Lorentz equations, are fundamental laws of physics.
They underpin our understanding of the relationship between electricity and magnetism, and are among the essential, fundamental laws of modern physics.

There are 4 forms of Maxwell's equations:
- The Maxwell-Gauss equation
- The Maxwell-Thomson equation
- The Maxwell-Faraday equation
- The Maxwell-Ampere Equation
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics (also known as the Carnot principle after its discoverer, in 1824) proves irrefutably that physical phenomena are irreversible, especially when thermal changes occur.
The principles of thermodynamics are the principal laws governing thermodynamics.
This principle has been modified and reformulated on several occasions, and gained widespread popularity in 1873 thanks to Ludwig Boltzmann and Max Planck.

While the first law of thermal dynamics specifies that energy can be exchanged between physical systems as heat and work. The second law introduces another quantity, known as entropy.
It is a principle of change and evolution since it determines in which direction potential energy transformations are possible.
Therefore, some chemical transformations are possible while others will never be. You can state with certainty, for example, that if you put an ice cube in a cup of hot coffee, the ice cube will melt, while the coffee will never freeze.
The Schrödinger Equation
The Schrödinger equation, conceived by the Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger in 1925, is a fundamental equation in quantum mechanics.
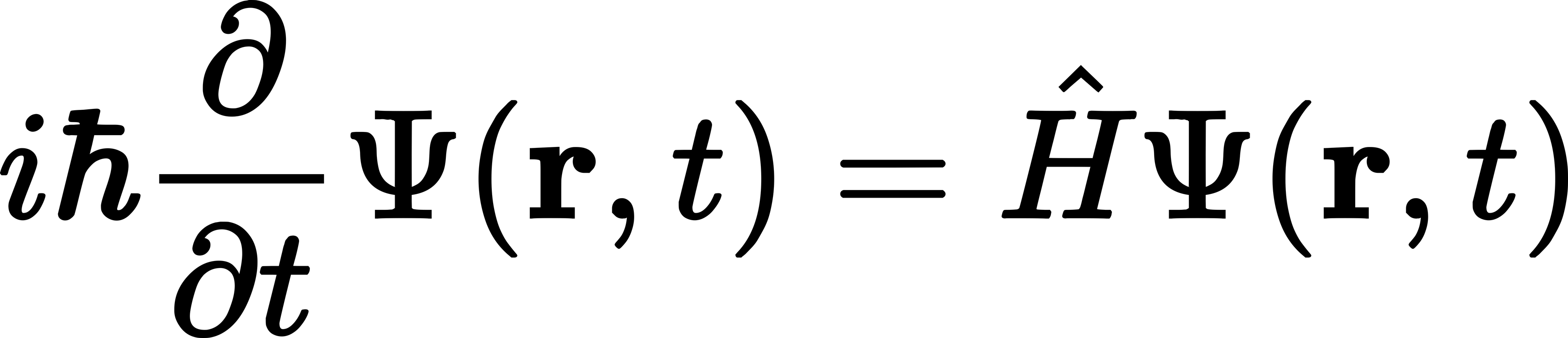
As Einstein's theory of general relativity helped explain the universe on a large scale, this equation sheds light on the behaviour of atoms and subatomic particles.
The Schrödinger equation explains the changes over time of a particle. It describes the states of a particle, from which it is possible to describe any state.
This equation poses a real philosophical question: Is matter made up of the presence of possible physical states (solids, liquids, gases)?
Discover qualified maths tutors near me here on Superprof.
The application of this equation can be found in modern technology including nuclear energy, solid-state computers and lasers.
As we can see, throughout human history and especially since the 18th century, mathematical equations have transformed our understanding of the world in which we live and our ability to solve maths problems. They serve us every day in our daily lives, in maths lessons or in more or less direct means.
Formulas and equations you may learn about in algebra lessons are quadratic formulae, simultaneous equations, differential equations, multi-step, two-step, and one-step equations, polynomial equations, linear equations, exponential functions, as well as systems of equations.
Prizes And Awards For Maths
There are a number of integral awards given to people, often nicknamed geniuses, who excel in various areas of mathematics, usually offering a solution to a math problem. These are prestigious awards with absolute value and worth, some of which are even thought to be equivalent to winning the Nobel Prize. As such, only a very select few receive these awards highlighting their mathematical excellence.
Below are some of these awards.
The Fields Medal
The Fields Medal is one of the most famous prizes given to mathematicians who have achieved something amazing during their career working with numbers, equations or more, such as discovering a significant theory or concept.
Officially, winners of this prize are awarded the International Medal for Outstanding Discoveries in Mathematics (you can see why this is more commonly referred to as simply the Fields Medal) and it is only given out once every four years to up to four mathematicians below 40 years of age. This means that most winners of this prestigious award can be classed as young, up-and-coming mathematicians with much promise for the future.
Abel Prize
Yet another reputable nomination, the Abel Prize is presented by the King of Norway to a mathematician who is outstanding in their field of mathematic study.
It is named after Niels Henrik Abel who, back in 2001 when it was first created, was a popular Norwegian mathematician.
Wolf Prize in Mathematics
The Wolf Foundation of Israel awards six different prizes each year, one of which being the Wolf Prize in Mathematics.
This award has been in existence since 1978 and is seen as a great honour to the nominee. Some well-known names who have won this award include Andrew Wiles, John Milnor and others.
Chern Medal
One of the newer prizes in mathematics is the Chern Meda, which has been recognising lifetime achievements for maths since 2010.
It is awarded every four years, so only a handful of mathematicians have got their hands on one of these prestigious awards so far. It is given out at the International Congress of Mathematicians and it includes a monetary prize of $250,000 (evidently to help fund further research or to enhance tuition in other fields of mathematics).
The first recipient in 2010 was Louis Nirenberg and the 2014 winner was Phillip Griffiths.
So why is there no Nobel prize for mathematicians?
In the world of math facts, some would say that the reason for this is because Alfred Nobel's wife had an affair with a famous mathematician, yet we now know this not to be true as Nobel didn't even marry during his lifetime. Put simply, his work involving scientific matters meant that he had those subjects closer to his heart than mathematical expression.
Get help learning this important subject and find maths tutors near me on Superprof.
Summarise with AI:
















Round O’ Clock Very Interesting.
Thank you for your positive comment!