Pure mathematics is, in its way, the poetry of logical ideas. - Albert Einstein
The history of mathematics explores the origins of mathematical discoveries, as well as the methods and notation used in the past. Before the modern era and the widespread dissemination of knowledge, written evidence of new mathematical advancements was limited to a few specific regions. Around 3000 BC, the Mesopotamian states of Sumer, Akkad, and Assyria, along with Ancient Egypt and the Levantine state of Ebla, began using arithmetic, algebra, and geometry for taxation, commerce, trade, and astronomical record-keeping.
The earliest known mathematical texts come from Mesopotamia and Egypt, including the Plimpton 322 (Babylonian, c. 2000-1900 BC), the Rhind Mathematical Papyrus (Egyptian, c. 1800 BC), and the Moscow Mathematical Papyrus (Egyptian, c. 1890 BC).
These texts all reference Pythagorean triples, suggesting that the Pythagorean theorem is one of the oldest and most widespread mathematical developments after basic arithmetic and geometry.
The exploration of mathematics as a "demonstrative discipline" originated in the 6th century BC with the Pythagoreans.
They created the term "mathematics" from the ancient Greek μάθημα (mathema), which translates to "subject of instruction." Greek mathematics significantly improved the methods, particularly through the use of deductive reasoning and mathematical rigor in proofs, and broadened the scope of mathematical topics.
The history of mathematics is a fascinating journey that spans thousands of years, shaping how we understand and interact with the world around us. It is a story of discovery, innovation, and the brilliant minds that paved the way for modern mathematical concepts.
- The history of maths or its origin can be traced back to ancient civilizations. The Babylonians, around 2000 BCE, developed a sophisticated system of mathematics, including methods for solving quadratic equations. They also introduced the concept of the number zero.
- In ancient Greece, mathematical thinking took a philosophical turn. In the 6th century BCE, Pythagoras laid the foundation for geometry, famously formulating the Pythagorean theorem. Euclid, around 300 BCE, compiled "Elements," a comprehensive collection of mathematical knowledge that remained a standard textbook for over two thousand years.
- During the Golden Age of Islam, from the 8th to the 14th centuries, mathematicians like Al-Khwarizmi and Ibn al-Haytham made remarkable contributions. Al-Khwarizmi's work on algebra laid the groundwork for modern algebraic notation, and his book "Al-Kitab al-Mukhtasar fi Hisab al-Jabr wal-Muqabala'' introduced systematic methods of solving linear and quadratic equations.
- The Renaissance period in Europe saw a resurgence of mathematical inquiry. Mathematicians like Leonardo Pisano, better known as Fibonacci, introduced the Hindu-Arabic numeral system to Europe, revolutionizing arithmetic calculations.
- In the 17th century, Isaac Newton and Gottfried Leibniz independently developed calculus, revolutionizing how we understand change and motion—this period marked a pivotal moment in the development of modern mathematics.
- The 19th and 20th centuries witnessed a flurry of mathematical breakthroughs. Georg Cantor introduced the concept of set theory, paving the way for modern formal mathematics. Albert Einstein's theory of relativity and the advent of quantum mechanics brought about profound mathematical challenges and advancements.
Today, mathematics is a cornerstone of science, technology, engineering, and other fields. From computer algorithms to cryptography, from understanding the universe's structure to modeling complex systems, mathematics continues to shape our world profoundly, building upon a rich history of human inquiry and discovery.
Need help learning mathematical concepts? Find online maths tuition here on Superprof!
By 3000 BCE, the Sumerians had created a numerical system using base 60, known as the sexagesimal system, which is still utilized for measuring time such as seconds, minutes, and degrees in a circle. Additionally, they made advancements in the fields of geometry, algebra, and arithmetic.

Who Discovered Maths?
It is a common misconception that a certain individual must have invented math. People often wonder who invented Maths, but Mathematics is a fundamental language of logic and numbers. It wasn't "invented" by any individual but developed over millennia by various civilizations. It emerged as a natural response to human needs for counting, measuring, and understanding the world.
Ancient civilizations like the Babylonians, Egyptians, and Greeks significantly contributed to mathematical knowledge. The Greeks, for instance, laid the groundwork for geometry through the works of mathematicians like Euclid.
However, the modern mathematical system we use today, including the decimal system and concepts like zero, originated in ancient India. Mathematicians like Brahmagupta and Aryabhata made pivotal advancements in arithmetic and algebra.
In the Islamic Golden Age, scholars like Al-Khwarizmi formalized systematic methods for solving equations, laying the foundation for algebra.
So, while no person "invented" mathematics, it evolved through collaborative efforts across cultures and centuries, each adding crucial building blocks to the mathematical edifice we know today.
Origin and Development of Maths
Mathematics, often considered the language of the universe, has a rich and intricate history that spans millennia. Its origins can be traced back to the earliest human civilisations, where the need for counting, measuring, and understanding the world around them gave birth to basic mathematical concepts. Let’s understand the origin and development of maths over the ages.
History Of Mathematics - Timeline
Did you know?
Around 600 BCE, the Greeks took a philosophical approach to mathematics. Pythagoras and his followers established the Pythagorean theorem, foundational in geometry. Euclid, around 300 BCE, compiled "Elements," a comprehensive collection of mathematical knowledge that became a standard textbook for over two thousand years.


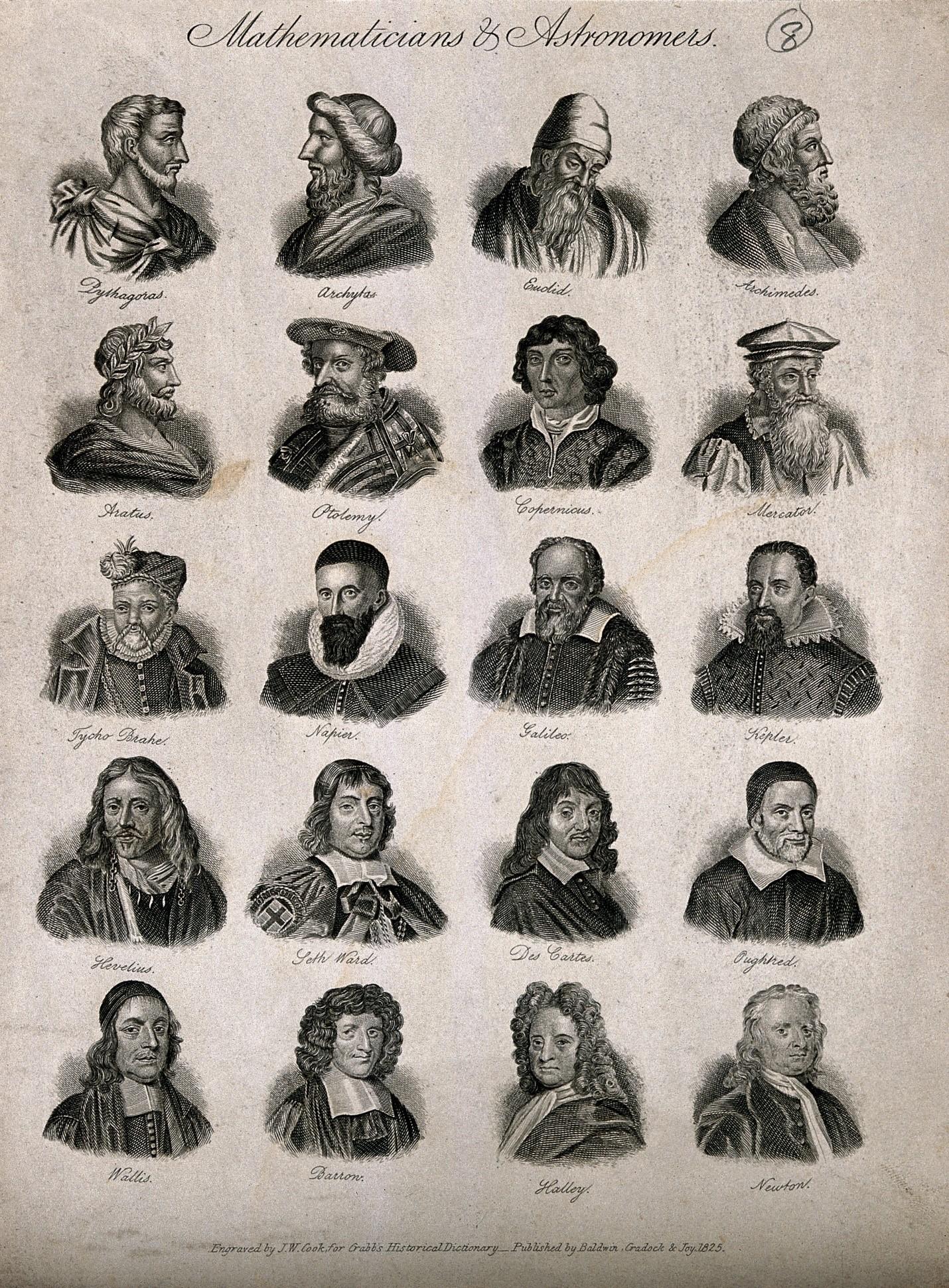
Evolution Of Mathematics - Famous Mathematicians!
Did you know?
The earliest known mathematical texts date back to around 2000 BCE in Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq). Babylonian mathematicians used a base-60 numeral system and made significant advances in geometry and algebra.
Euclid: Often referred to as the "father of geometry," Euclid's "Elements" laid down the foundations of geometry as a systematic study.
Pythagoras: Pythagoras and his followers made significant contributions to geometry, particularly the famous Pythagorean theorem.
Al-Khwarizmi: A Persian mathematician who worked in the House of Wisdom in Baghdad, he is considered one of the fathers of algebra.
Ibn al-Haytham: Made important contributions to optics and mathematics, including the development of algebraic methods.
Leonhard Euler: An 18th-century mathematician who made significant contributions to graph theory, topology, and number theory.
Rene Descartes: Often credited with the development of Cartesian coordinates and analytic geometry.
Gauss: A mathematician who made contributions to number theory, algebra, statistics, and differential geometry.
Cantor: Known for his work on set theory and the development of the concept of infinity.
Einstein: Although a physicist, his contributions to the understanding of space and time had profound implications for the field of mathematics.
Find a qualified tutor on Superprof to help you learn everything you need for maths class!
Maths in Vedas
The Vedas, ancient texts of knowledge from India, contain profound insights into various fields, including mathematics. Though primarily focused on spiritual and philosophical wisdom, the Vedas also demonstrate a deep understanding of numerical concepts and mathematical principles. Here, we have unveiled more about Maths in Vedas.
Number Systems
In the Rigveda, one of the oldest Vedic texts, we find references to numbers and their significance. The concept of large numbers, up to the magnitude of trillions, is present. This indicates a high level of numerical proficiency.
Geometry and Measurement
The Yajurveda, another Vedic text, references geometric shapes and measurements. It discusses concepts like the circumference of a circle, the diagonal of a square, and even the value of pi.
Arithmetic Operations
The Atharvaveda contains verses that deal with mathematical operations. It includes methods for addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. These practical aspects of mathematics are evident in rituals and sacrifices described in the Vedas.
Rituals and Astronomy
Mathematics was integral to Vedic rituals and astronomical calculations. Precise measurements were crucial for determining auspicious ritual times and understanding celestial movements.
Sulba Sutras
These are appendices to the Vedas that focus specifically on geometry and mathematics. They provided instructions for constructing various altars and fireplaces for rituals requiring precise measurements and geometric shapes.
Concept of Infinity
The concept of infinity is subtly embedded in Vedic thought. The idea of the infinite, unbounded universe is reflected in philosophical discussions.
Philosophical Significance
In addition to practical applications, mathematics in the Vedas holds philosophical significance. It symbolises the harmony and orderliness of the universe, reflecting the cosmic balance that ancient Indian philosophy often emphasised.
While the Vedas primarily focus on spiritual and philosophical themes, their inclusion of mathematical knowledge showcases the holistic nature of ancient Indian wisdom. It reveals a sophisticated understanding of numbers, geometry, and arithmetic woven into Vedic culture's fabric. These mathematical insights not only aided practical aspects of life but also contributed to the broader intellectual heritage of ancient India.
Today's Mathematics: Calculation and Analysis

In the contemporary era, mathematics is crucial in various aspects of our daily lives, ranging from simple calculations to complex data analysis. Here's a brief overview of how mathematics is applied today:
Everyday Calculations
Basic arithmetic, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, is fundamental to daily life. Whether it is calculating expenses, measuring ingredients for a recipe, or determining travel distances, these operations are constantly used.
Finance and Economics
In the realm of finance, mathematics is indispensable. It is used for budgeting, calculating interest rates, managing investments, and analysing economic trends. Concepts like compound interest and statistical analysis are vital tools in financial decision-making.
Science and Engineering
Mathematics underpins all branches of science and engineering. From physics to biology, mathematics is essential for formulating theories, modelling natural phenomena, and solving complex equations. Engineers use mathematics to design structures, analyse materials, and optimise processes.
Technology and Computing
In the world of technology, mathematics is foundational. Computer science relies heavily on algorithms and discrete mathematics for coding, data storage, and encryption tasks. Mathematics also powers the algorithms behind search engines, social media platforms, and other digital tools.
Statistics and Data Analysis
In an era of big data, statistical analysis is crucial for making sense of vast information. From market research to medical studies, statistical methods are used to draw meaningful conclusions and make informed decisions.
Cryptocurrency and Blockchain
The rise of cryptocurrency relies on complex mathematical algorithms for secure transactions and record-keeping through blockchain technology. Concepts from number theory and cryptography play a vital role in this field.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Mathematics is the backbone of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Algorithms and mathematical models enable machines to learn patterns, make predictions, and perform tasks once thought to be exclusively human.
Space Exploration and Astronomy
Mathematics is integral to space exploration. Calculations involving orbits, trajectories, and celestial mechanics are essential for planning missions to other planets and understanding the universe's vastness.
Medicine and Healthcare
In medicine, mathematics is used for tasks such as medical imaging, modeling disease spread, and conducting clinical trials. It aids in diagnosing conditions, developing treatments, and understanding health trends.
In today's world, mathematics is not only a tool for solving problems but a foundation for innovation, discovery, and progress across various disciplines. Its applications are far-reaching, from our daily routines to the most advanced scientific and technological endeavors.
In conclusion, the role of mathematics in our modern world is nothing short of extraordinary. It permeates every facet of our lives, from the simplest calculations that guide our everyday decisions to the complex algorithms that power the most advanced technologies. Mathematics is the language of science, the cornerstone of engineering, and the driving force behind innovation. Its application in fields like finance, medicine, and space exploration continues to shape the trajectory of human progress.
Furthermore, as we navigate an era of big data and artificial intelligence, mathematics stands as the bedrock of understanding and harnessing information on an unprecedented scale. It empowers us to make sense of the vast digital landscape, uncovering patterns, and extracting meaningful insights.
In essence, mathematics facilitates problem-solving and fuels our curiosity, enabling us to explore the boundaries of knowledge and imagination. It is the bridge between the theoretical, practical, conceptual, and tangible. With its enduring relevance, mathematics remains an essential tool for navigating the complexities of our modern world and unlocking the boundless potential of the future.
Summarise with AI: