From the enigmatic algorithms of ancient texts to the cutting-edge theories of modern mathematicians, the evolution of maths in India is a tapestry woven with centuries of ingenuity, insight, and cultural exchange. India's mathematical heritage is a testament to the intellectual prowess of its ancient scholars and their enduring legacy in shaping the global mathematical landscape.
Dating back to the Indus Valley Civilisation, India's mathematical journey began with rudimentary number systems and geometric knowledge. Over millennia, it evolved alongside the rise and fall of empires, absorbing influences from diverse cultures and contributing its unique insights to the mathematical world.
This exploration will embark on a fascinating journey through the epochs of Indian mathematics, shedding light on the profound contributions of luminaries like Aryabhata, Brahmagupta, and Bhaskara, who paved the way for groundbreaking discoveries in areas ranging from number theory to geometry. Here, you can traverse the medieval period, which saw the flourishing of Kerala School and the advent of innovative techniques, such as the famed Kerala School of Astronomy and Mathematics, which revolutionised calculus and infinite series.
Continuing into the colonial era, one can uncover the intersection of Indian and European mathematical traditions, exemplified by Srinivasa Ramanujan, whose enigmatic formulas challenge mathematicians worldwide. Moving into the modern era, it's interesting to explore India's role in developing applied mathematics and computer science and its prominent standing in the global mathematical community.
Through this odyssey, observers will witness how Indian mathematics, characterised by its holistic approach and profound philosophical underpinnings, has left an indelible mark on the world of numbers, equations, and proofs. Here, you can read the story of mathematics in India, its evolution and the influence of this ancient mathematical tradition.

Story of Mathematics in India
Imagine a time long ago when people didn't have fancy calculators or computers. They had to figure things out using their brains and simple tools. This is where the story of mathematics in India begins.
Ancient Beginnings
Around 2600 BCE, people were already using basic numbers and shapes in a place called the Indus Valley. They needed this knowledge for things like trading goods and building houses. They made special symbols to represent numbers, like today's numbers.
Clever Ideas from Ancient Thinkers
As the years passed, wise people in India started developing more advanced ideas. Aryabhata, who lived around the 5th century CE, was one of them. He wrote books with amazing discoveries about numbers, like how to find the area of a triangle and the value of a circle's constant (like π in our math today).
Inventions that Still Amaze Us
Another thinker, Brahmagupta, was like a math superstar in the 7th century. He figured out how to solve quadratic equations (which involve x², like x² - 4x + 4 = 0) and even introduced the idea of zero as a number. Zero is a big deal in math!
The Kerala School and Calculus
Fast forward to medieval times, when a group of clever minds in Kerala, India, created their math revolution. They were like the pioneers of calculus, a math that helps us understand how things change over time. They used it to study the movement of planets and stars.
Srinivasa Ramanujan: The Math Wizard
Jumping to more recent times, there's Srinivasa Ramanujan. He lived in the early 20th century and was a math genius. He had a special talent for finding cool math formulas that seemed to come out of nowhere. Even today, his ideas are studied by mathematicians all around the world.
India's Role in Modern Math
Nowadays, India is a big player in the world of math. Many Indian mathematicians are doing incredible research, from figuring out how computers work to solving complex problems in number theory.
History of Aryabhatta Discovery of Zero

Long ago, in ancient India, a brilliant mathematician and astronomer named Aryabhatta made a discovery that would change the world of mathematics forever. He is known for introducing the revolutionary concept of "zero." Here is the history of Aryabhatta discovery of zero:
Need for a Placeholder
In Aryabhatta's time, around the 5th century CE, people already used numbers for various purposes. They counted things, measured land, and kept track of time. However, they faced a challenge: there wasn't a special symbol representing nothing or "zero." Imagine trying to write down numbers without a zero! It's like trying to write a story without spaces between words. It quickly becomes confusing and hard to understand.
Birth of Zero
Aryabhata, a brilliant mathematician and astronomer, changed this. In his famous work "Aryabhatiya," he introduced a symbol for zero, which he called "sunya." This word meant "empty" or "void." This was groundbreaking because it marked the beginning of the zero we know and use in mathematics today.
A Revolutionary Idea
Zero was a game-changer in the world of mathematics. Before the concept of zero, performing complex calculations and advanced math took a lot of work. Imagine expressing a large number like 1,000 without zero—it's not easy! Zero acted as a placeholder, making it much easier to write and understand numbers, especially large ones.
Zero's Impact on Math and Science
Aryabhata's idea of zero was unrestricted to India. It spread to other parts of the world, reaching places like the Middle East and Europe. This had a profound impact on mathematics, science, and even astronomy. With zero as a tool, calculations became more precise, and scientists could explore new frontiers in understanding the universe.
Foundation of Our Number System
Today, our number system relies heavily on the concept of zero. It's hard to imagine doing math without it. Zero is fundamental in various calculations, from simple addition to complex algebra. It's woven into the fabric of our mathematical language.
Aryabhata's Legacy
Aryabhata's contribution to mathematics was so remarkable that he is often hailed as one of the pioneers of the number system we use today. His ingenious idea of zero has become an essential building block of mathematics. We owe him a great deal for making our lives in the world of numbers so much easier. His legacy lives on, reminding us of the power of innovative thinking and the enduring impact of a single idea.
So, next time you see the number zero, remember Aryabhata, the Indian mathematician who gave us this amazing invention that changed how we count, calculate, and understand the world of numbers. It proves that even the simplest ideas can have the most profound impact!
Development of Maths

From ancient civilisations crafting rudimentary number systems to the groundbreaking theories of modern mathematicians, the evolution and development of maths mirror humanity's intellectual progress.
Vedic Mathematics
The roots of mathematics in India can be traced back to the ancient Vedic period, which lasted from around 1500 BCE to 500 BCE. The Vedas, ancient Indian scriptures, contained mathematical knowledge that was incredibly advanced. Vedic scholars devised techniques for mental calculations, now known as Vedic Mathematics. These methods were intuitive and efficient, making complex calculations surprisingly straightforward.
Brahmagupta and Early Advances
Moving forward, around the 7th century CE, a remarkable mathematician named Brahmagupta made significant contributions. He wrote the famous mathematical treatise called the "Brahmasphutasiddhanta", where he discussed rules for arithmetic operations, including zero and negative numbers. This was a groundbreaking development that greatly influenced the future of mathematics not only in India but worldwide.
Medieval Kerala School
The medieval period in India witnessed the emergence of the Kerala School of Mathematics and Astronomy, roughly from the 14th to 16th centuries. This school of thought made remarkable strides in trigonometry, calculus, and algebra. They even developed methods for calculating π and made pioneering contributions to infinite series, concepts that would later play a crucial role in the development of modern calculus.
Srinivasa Ramanujan
Jumping to the early 20th century, India gave birth to one of the most prodigious mathematical talents in history - Srinivasa Ramanujan. Largely self-taught, Ramanujan's work in number theory, infinite series, and continued fractions was nothing short of extraordinary. His contributions to mathematics were so significant that even today, his theorems and formulas are subjects of extensive study and research by mathematicians globally.
Modern Era and Beyond
As India moved into the modern era, it substantially contributed to mathematics. Indian mathematicians have excelled in various fields, including number theory, algebra, and applied mathematics. The country has also played a vital role in developing computer science and information technology, which rely heavily on mathematical principles.
Legacy and Influence
The legacy of Indian mathematics endures through the ages. The foundational concepts, innovative techniques, and profound philosophical underpinnings continue to shape how we understand and use mathematics in the present day. India's mathematical journey, starting from the ingenious methods of Vedic mathematics, has left an indelible mark on the global mathematical community, showcasing the enduring brilliance of Indian mathematicians throughout history.
Discover maths tutors near me on Superprof and make sure you understand all the mathematics concepts!
Modern Mathematics and its Application in Different Sectors
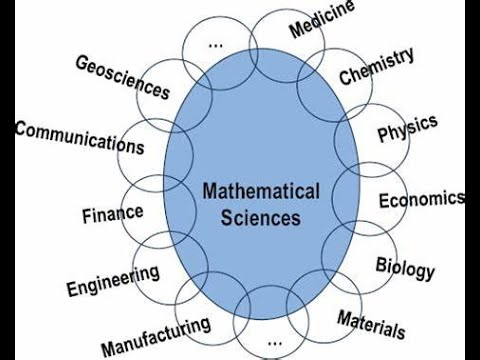
Mathematics is the silent engine that powers our modern world. Its applications span various sectors, influencing everything from technology to finance, science, engineering, and even the arts. Here's a detailed look at the myriad ways in which mathematics plays a pivotal role in our daily lives:
Technology and Computing
Software Development: Algorithms and coding, at their core, are mathematical constructs. They form the basis for all software applications and are crucial in building everything from simple mobile apps to complex operating systems.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): These cutting-edge fields rely heavily on mathematical principles, particularly statistics and linear algebra, to train models and make predictions based on data.
Finance and Economics
- Banking and Investments: Calculations involving interest rates, investments, and financial risk assessments are deeply rooted in mathematical concepts like calculus, statistics, and probability theory.
- Stock Market Analysis: Traders and analysts use mathematical models to predict market trends and make informed investment decisions.
Engineering
- Civil Engineering: Engineers use mathematical principles to design structures, calculate load-bearing capacities, and plan construction projects.
- Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Math is essential for designing circuits, calculating voltage and current flows, and developing advanced electronic devices.
Physics and Sciences
- Astronomy: From calculating orbits to predicting celestial events, mathematics forms the backbone of astronomical research.
- Chemistry: Mathematical models are used to understand chemical reactions, predict behaviour of molecules, and analyse experimental data.
Medicine and Healthcare
- Medical Imaging: Techniques like MRI, CT scans, and X-rays rely on mathematical algorithms for image reconstruction and interpretation.
- Epidemiology: Mathematical models are used to analyse the spread of diseases and predict future outbreaks.
Architecture and Design
- Architects use geometry, calculus, and engineering mathematics to create aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound buildings.
Transportation, Logistics and Telecommunications
- Mathematical optimisation models plan efficient routes, minimise transportation costs, and optimise supply chain operations.
- The design and optimisation of communication networks rely on mathematical concepts like graph theory and signal processing.
Environmental Sciences
- Mathematical models are used to predict and analyse climate patterns, study ecosystems, and evaluate the impact of human activities on the environment.
Arts and Entertainment
- Computer Graphics: In the world of computer graphics, mathematics plays a fundamental role. Geometric transformations, such as rotations and translations, are applied to create 3D models. Shading, lighting, and texture mapping algorithms rely heavily on mathematical concepts like vectors and matrices. These techniques bring lifelike visuals to movies, video games, and virtual reality experiences.
- Animation: Animators use mathematics to generate movement. Concepts like keyframes and interpolation use mathematical functions to create smooth transitions between frames. Physics-based simulations, which govern the movement of objects or characters, rely on equations of motion.
- Digital Art: Mathematical algorithms are employed in generative art, where computer programs use mathematical rules to create unique and intricate patterns. Fractals, for instance, are mathematical sets that generate complex and visually captivating images. Artists use algorithms to explore creativity and generate unique visual expressions.
Education and Research
- Sociology: Statistical analysis is crucial to gathering and analysing data on social trends, demographics, and behaviour. Researchers use techniques like regression analysis to understand relationships between different variables.
- Linguistics: Mathematics, particularly statistics, aids in linguistic research by analysing large datasets of language usage. This includes studying patterns in speech, word frequencies, syntactic structures, and phonetics.
- Psychology: Researchers use statistical methods to analyse experiments and studies, concluding human behaviour and mental processes. This helps make informed decisions in clinical psychology, cognitive psychology, and behavioural analysis.
- Economics: Mathematical modelling is central to economic research. Economists use advanced mathematical techniques to model economic systems, predict market behaviour, and analyse the impact of policy decisions.
- Political Science: Statistics analyse voting patterns, public opinion polls, and various political phenomena. This data-driven approach helps political scientists understand political behaviour and make informed interpretations.
- Education Research: Statistical analysis evaluates the effectiveness of different educational strategies, programs, and interventions. This research informs policy decisions and helps improve teaching methods.
- Environmental Studies: Mathematical models simulate and predict environmental processes, such as climate change, pollution dispersion, and ecological interactions. These models guide environmental policies and conservation efforts.
Mathematics is a powerful tool for analysis, modelling, and prediction in these diverse fields. It enables researchers and professionals to make evidence-based decisions, uncover patterns, and advance knowledge in their respective domains. Mathematics, therefore, forms an integral part of the foundation upon which advancements in these fields are built.
Summarise with AI: