There are several languages spoken in India, and Tamil is one of the oldest classical languages still in use. Tamil is one of the oldest languages in the world, not just in India. The intriguing history of the Tamil language provides a clear window into how Southern India has changed over time. The first and official language of Tamil Nadu, Tamil is also one of the official languages of Pondicherry and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, two union territories.
Due to its widespread usage, the Tamil language has been granted official status in Singapore, India, and the northeastern region of Sri Lanka. Tamil is one of the 23 officially recognized languages in India, and there are roughly 60 million speakers of the language worldwide. In 2004, it became the first Indian language to be designated as a "classical language" by the Indian government. Tamil is a widely recognized language in society, and companies that are serious about expanding internationally use Tamil to communicate with Tamil-speaking customers.

How Old is the Tamil Language? A Brief History
Tamil belongs to the family of Dravidian languages, which also includes Telugu, Kannada, and Malayalam, spoken in India's southern areas. Tamil falls within the category of Southern Dravidian language (Teṉ tirāviṭa moḻi – தென் திராவிட மொழி).
Discover the fascinating story of Indian English.
Based on the language's geographic distribution and distinctive linguistic characteristics that set it apart from other Dravidian languages, this classification was made. Southern Dravidian languages are mostly spoken in Northern Sri Lanka, Singapore, and the southern parts of the Indian subcontinent, including the Indian states of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, and Puducherry.
Although the exact roots of the Tamil language are unknown, it is thought to have developed from a proto-Dravidian language that the ancient inhabitants of the area spoke. The Sangam period, which lasted from the third century BCE to the third century CE, is when the Tamil language first emerged. Tamil saw tremendous usage in poetry, literature, and religious writings throughout this time, and the spoken language experienced substantial grammatical and lexical modifications.
Discover your perfect Hindi teacher on Superprof today!
Origin and Evolution of Tamil
The earliest known form of Tamil is called Old Tamil (Paḻaiya tamiḻ – பழைய தமிழ்), sometimes called Sangam Tamil. It dates from approximately 450 BCE to 700 CE.
The Tamil people were divided into three kingdoms at this time:
Pandya (Pāṇṭiya pēraracu – பாண்ட்யம்)
Chola (Cōḁa cāmrājyam – சோழ சாம்ம்ப்ப்ப்)
Chera (Cēra cāmrājyam – சேர சாம்ம்ட்ட்).
Sangam literature, a compilation of Tamil poetry and music, was also created during this period.
Due to its distinct grammar, Old Tamil was distinguished by the usage of noun inflexions, verb conjugations, and case endings. The language was widely utilized in literature, trade, and religious texts, where it was employed to convey intricate concepts and feelings.
Get acquainted with the sweetest language in India, that is, Bengali.
Tamil grammar and vocabulary saw major modifications throughout the 7th to 16th centuries during the Middle Tamil period (Naṭuttara tamiḻ – நடுத்தர தமிழ்). The Chola dynasty gained popularity at this time, and Tamil literature flourished under their influence.
The disappearance of case endings, the rise of a more analytical grammar, and the streamlining of verb conjugations are characteristics of middle Tamil. During this time, Sanskrit terms were also introduced to Tamil (Tamiḻ coṟkaḷañciyam – தமிழ் சொற்களஞ்சியம்), enriching its lexicon and creating a distinct hybrid language called Manipravalam.
With the advent of modern Tamil (Navīṉa tamiḻ – நவீன தமிழ்), regular dialects and the establishment of Tamil as a literary language emerged about the sixteenth century.
The Tamil-speaking districts of South India were dominated by the Vijayanagara Empire throughout this time, and the language experienced additional alterations to accommodate the shifting social and political conditions. Simplified grammar, the usage of European language loanwords, and the adoption of a uniform script are characteristics of modern Tamil.
Tamil has remained a dynamic and lively language with a rich cultural legacy despite centuries of changes in vocabulary and grammar. The Tamil language is a source of pride and identity for the people of Tamil Nadu, and it has made great contributions to the fields of philosophy, science, and literature.
Learn the history of the Telugu language.
Literary Tamil vs. Informal Tamil
Spoken Tamil and literary Tamil are the two primary varieties of the Tamil language. The dialect of Tamil that is spoken in casual settings and in daily interactions is known as colloquial spoken Tamil. Naturally, this dialect of Tamil has changed over time to accommodate shifting social and cultural standards in the Tamil-speaking areas. It is distinguished by the usage of regional dialects, simplified grammar, and borrowed terms from other languages.
Literary Tamil, on the other hand, is the formal written form of Tamil that is utilized in formal contexts, academic work, and literature. It is more standardized than spoken Tamil and adheres to tight grammatical and syntactical standards. Literary Tamil is utilized in academic and scientific writing, as well as in the creation of both modern and ancient Tamil literature.
Modern spoken Tamil and literary Tamil are significant varieties of the language that add to the rich cultural legacy of the Tamil-speaking community, despite their distinctions. The differences between the two varieties of Tamil also demonstrate how dynamic the language is and how it can change through time to meet the requirements of its people.
Uncover another language steeped in heritage with a history of the Marathi language.
Writing System in Tamil
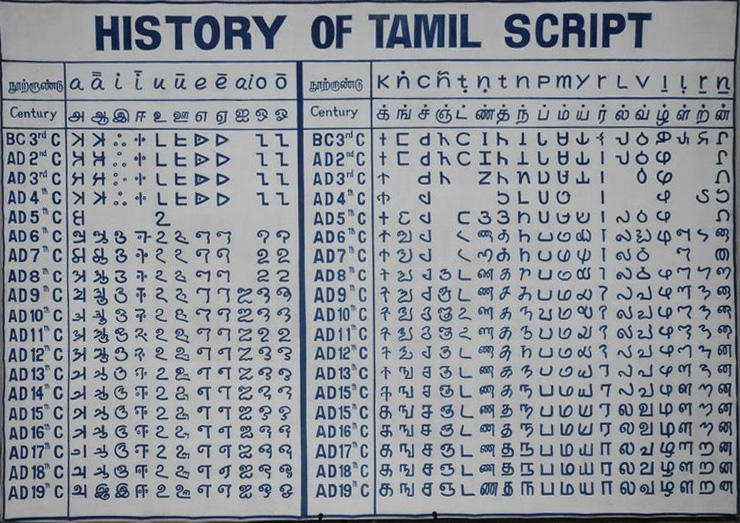
This classical language has one of the most intricate and ancient writing systems in the entire globe. The Brahmi script, which was in use in ancient India, is thought to have given rise to the Tamil script. Because it is a syllabic system, each symbol in the Tamil Brahmi script represents a syllable rather than a single letter, making it unique.
Twelve vowels and eighteen consonants make up the modern Tamil script, which is used to create various syllables. The vowels appear before the consonants in a particular order of arrangement between the vowels and consonants. Additionally, the script contains a variety of diacritical marks that can be used to alter vowel and consonant pronunciation.
Modern literary Tamil has extremely complicated grammar and syntax, with several rules controlling sentence construction and the usage of verbs, nouns, and other speech constituents in written language. The usage of gender markers for nouns and tense markers are two grammatical characteristics of the Tamil language that set it apart from other languages.
This classical language has a phonology that is distinct from other languages, having certain vowel and consonant sounds that are unique to it. The various vowels and consonants in the alphabet are combined to create the 216 distinct sounds that make up the Tamil language.
The Tamil alphabet actually has a total of 247 letters!
Tamil Numbers 1-10
One - ஒன்று (Ondru)
Two - இரண்டு (Irandu)
Three - மூன்று (Moondru)
Four - நான்கு (Naangu)
Five - ஐந்து (Aindhu)
Six - ஆறு (Aaru)
Seven - ஏழு (Ezhu)
Eight - எட்டு (Ettu)
Nine - ஒன்பது (Onpathu)
Ten - பத்து (Pathu)
Discover online Hindi classes on Superprof!
How to Learn Tamil Language
Including Tamil in your everyday life is the simplest approach to learning the language. This implies that you ought to make an effort to speak Tamil in your regular conversations. For instance, you can attempt to welcome your Tamil-speaking friends in Tamil or place an order for meals in a Tamil restaurant.

Speaking with Tamil speakers who are natural speakers is another method of learning the language. You can get better at grammar and pronunciation by doing this. Programs for Tamil language exchange are available online and in your neighbourhood. Through these programs, you can meet others who are interested in learning Tamil from native speakers.
Ultimately, learning Tamil requires perseverance and patience. Acquiring proficiency in a new language is a process that may require some time to complete. But you can get more proficient in Tamil and speak clearly in it with perseverance and practice.
Discover royalty with a concise history of the Urdu language.
Using a language study app is an excellent additional method for learning Tamil. You may learn Tamil with the aid of a variety of language-learning applications. Rosetta Stone, Babbel, and Duolingo are a few of the well-known ones. These applications offer interactive lessons that are intended to make learning Tamil interesting and enjoyable.
You can join a Tamil language course if you'd rather study the language the old-fashioned way. Tamil language classes are available both offline and online at numerous colleges and language schools. The purpose of these courses is to teach you the fundamentals of Tamil vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation. They also allow you the chance to rehearse public speaking with other pupils.
Interested in learning about Hindi? Find Hindi classes near me easily on Superprof!
Summarise with AI:
















