South India has been home to some of the greatest dynasties in Indian history, each leaving a strong legacy in art, architecture, literature, and administration. Here's a South Indian dynasties list with some of the most important empires and their respective periods:
- Chera Dynasty – c. 3rd century BCE to 12th century CE
- Chola Dynasty – c. 9th century CE to 13th century CE
- Pandya Dynasty – c. 4th century BCE to 16th century CE
- Pallava Dynasty – c. 3rd century CE to 9th century CE
- Satavahana Dynasty – c. 1st century BCE to 3rd century CE
- Vijayanagara Empire – c. 14th century CE to 17th century CE
- Hoysalas – c. 10th century CE to 14th century CE
In South India, a new era emerged following the later Vedic period. Records state that the beginning of dynastic authority in the south occurred during the Sangam era, which lasted from 300 BCE to the sixteenth century CE. Southern India was home to humans for thousands of years. Based on archaeological research, people lived in the Karnataka region's Hunsgi Valley approximately 1.27 million years ago. Let us jump ahead to the later Vedic and Sangam eras. Several kingdoms that were thriving at the same time emerged throughout this period. India's southern region was equally developed and rich as its northern counterpart.
Let's talk about all the major South Indian dynasties and their founders in more detail.

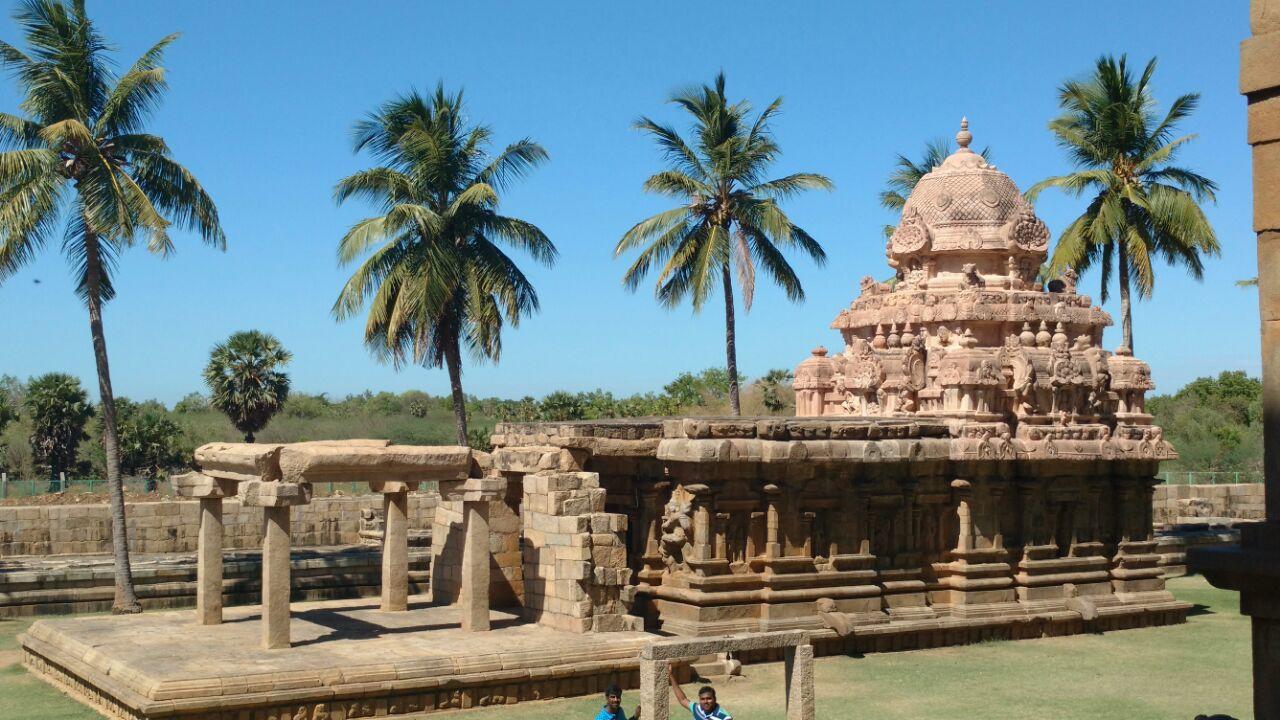
The Great Cholas
When fighting broke out between the Pallava and Pandya kingdoms in about 850 CE, the Cholas seized the chance. Following his conquest of Thanjavur (present-day Tanjore), King Vijayalaya renounced his title as Pallava emperor and proclaimed himself the new monarch. This marked the start of the Chola dynasty throughout the Middle Ages and the pinnacle of their power.
Growth of the Chola Kingdom
Under Rajaraja Chola's rule, the Chola Empire started to develop into a multiethnic trading powerhouse. He pushed the empire's northern frontier from Tamil regions to Kalinga in northeastern India, where he gained control of the Maldives and the affluent Malabar Coast on the subcontinent's southwest coast. These territories were strategic points on the Indian Ocean trade routes.
Rajendra Chola deposed the rulers of Bengal and Bihar by 1044, drew new borders up to the Ganges River (Ganga), and took control of significant ports in the Malay Peninsula, Indonesian archipelago, and Myanmar's coastal regions (Burma). It was the original maritime empire of India. The Chola Empire under Rajendra even demanded tribute from Siam (Thailand) and Cambodia. In terms of culture and the arts, Indochina and the Indian mainland were mutually affected.
However, during the Middle Ages, there was one major thorn in the side of the Cholas. The Chalukya Empire made repeated attempts to topple the Cholas in the western Deccan Plateau. Following decades of intermittent warfare, the Chalukya kingdom collapsed in 1190. However, the Chola Empire's gadfly did not last very long.
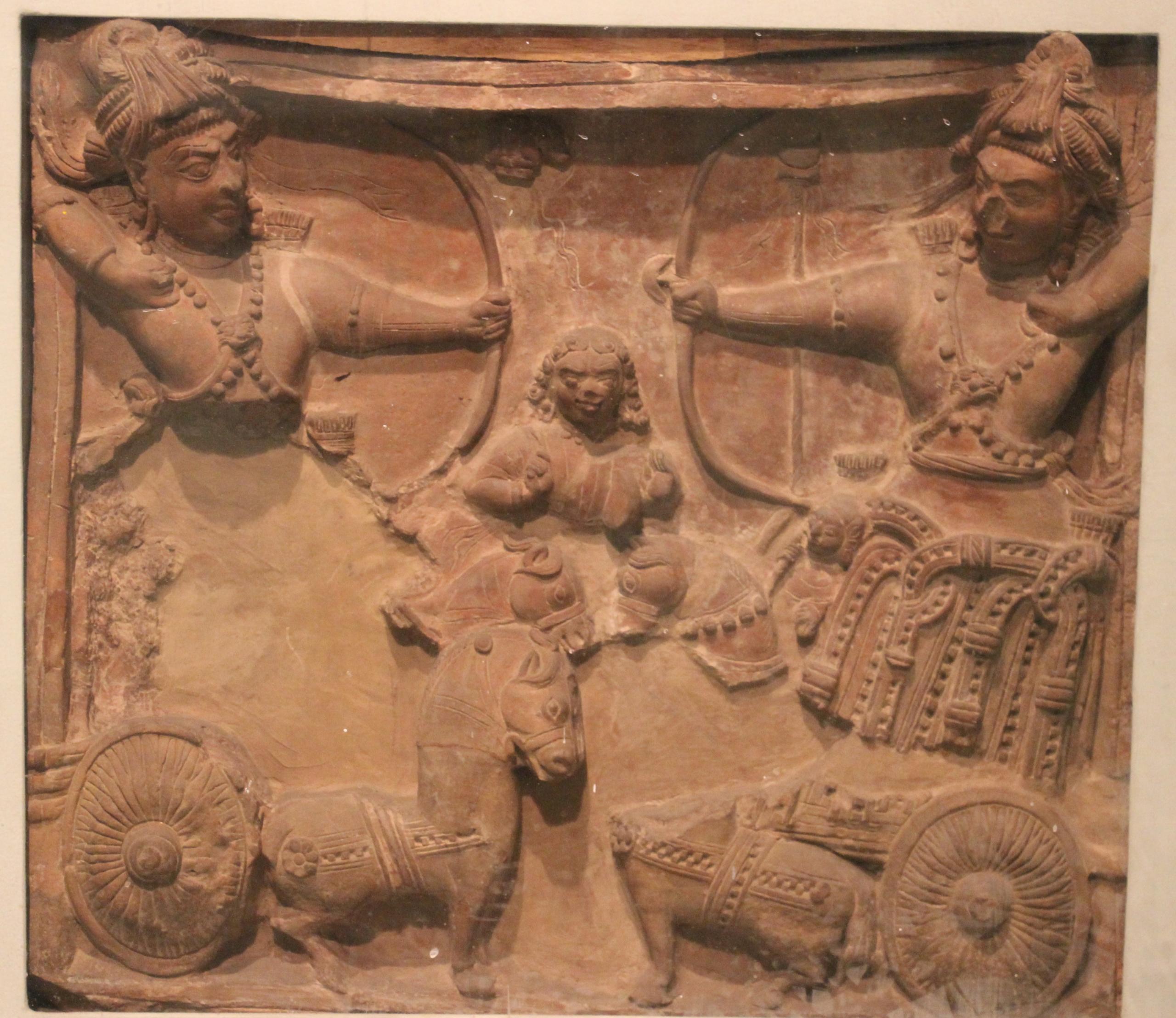
The Powerful Chalukyas
A large portion of southern and central India was governed by the Chalukya royal line from the sixth and the eleventh centuries. They governed as three distinct but connected dynasties during that period. The earliest dynasty was the Badami Chalukyas. They established their headquarters in Badami and rose to prominence in the middle of the sixth century. The Badami Chalukyas began to demand their freedom as the Kadamba kingdom of Banavasi crumbled.
They rose to prominence very fast under Pulakesin II's reign. Following Pulakesin II's demise, the Eastern Chalukyas established their kingdom in the eastern Deccan. They governed from their center, Vengi, until approximately the year 1100. In the ninth century, the Rashtrakutas of western Deccan became powerful before the Chalukyas of Badami. Their relatives, the Western Chalukyas, regained control only in the latter part of the eleventh century. Those Western Chalukyas ruled from Basavakalyan to the end of the 1100s.
The ascendancy of the Chalukyas was a watershed in the history of South India and a golden age for the state of Karnataka. Smaller kingdoms gave way to large empires in South India with the development of the Badami Chalukyas. For the first time in history, a nation from South India conquered and united the entire region between the Kaveri and Narmada rivers.
With the expansion of that kingdom came improved governance, increased trade and commerce with other nations, and the development of a brand-new architectural style known as Vesara. In the ninth century, Kannada gained prominence as a literary language in the Veerashaiva Vachanas, the Jaina Puranas, and Brahminical literature. When the Eastern Chalukyas came to power in the eleventh century, Telugu script started to take shape.

While historians dispute the origins of the Chalukya dynasty, most historians concur that the original Chalukyas originated in the Karnataka region. According to one idea, the Pallavas of Kanchi are believed to be descended from the ancient "Parthians," who are said to have been the progenitors of the Pallavas. The Chalukya, on the other hand, are said to have sprung from the "Seleukia" tribe in Iraq.
Some believe they descended from a different ancestor, a warrior from the second century known as Kandachaliki Remmanaka, who was a feudal subject of the Andhra Ikshvaku. The theory that the Eastern Chalukyas originated in the north is corroborated by another document about them. According to legend, an Ayodhya ruler defeated the Pallavas in the south and wed a Pallav woman. She was the mother of a child named Vijayaditya. A lot of people claim he fathered Pulakesin I. Inscriptions suggest that Runaranga was Pulakesin I's father.
The Chalukyas ruled over the Deccan plains in central India for approximately 600 years. They governed as three distinct but connected dynasties during that period. The Chalukyas of Badami ruled from the sixth to the ninth century. The Chalukyas of Vengi, often referred to as the Eastern Chalukyas, and the Chalukyas of Kalyani, also known as the Western Chalukyas, were also present.

The Mighty Rashtrakutas
The Rashtrakuta dynasty ruled over South India from the ninth to the eleventh century CE. At its height, their kingdom included large portions of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Maharashtra, Gujarat, and the modern state of Karnataka in India. Al-Masudi and Ibn Khordadbih (10th century CE) are two among the many Islamic scholars and travellers who report that the Rashtrakutas were so strong and influential that all other Indian monarchs at the time bowed down to them in respect and prayed to them as a higher force.
During that period, the Rashtrakutas were ruled by several different but related clans. Dating back to the seventh century, the earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription depicts their rule from Manpur, located in the Malwa area of modern-day Madhya Pradesh. It is located on a grant for copper plates. Inscriptions from the same era mention the monarchs of Kannauj, Achalapur, and modern-day Elichpur in Maharashtra, among other notable Rashtrakuta clans. There are differences in the language, origin, and lineage of the early Rashtrakutas.
Each of the three empires briefly annexed the capital at Kannauj as part of their struggle for control of the wealth of the Gangetic plains during the ninth and tenth centuries. During a time of political development, architectural wonders, and notable literary achievements, the Rashtrakutas of Manyakheta prospered. From the Yamuna and Ganga River delta in the north to Cape Comorin in the south, their vast realm spanned. The previous kings of that dynasty had been Hindu, while the later ones were heavily influenced by Jainism.

A woman called Rathika is mentioned in some of Ashoka's edicts (Mansera, Girnar, Dhavali) and may have been the ancestor of the Rashtrakutas. The inscriptions are said by many historians to allude to earlier Rathikas, which are thought by many to be the Rashtrakutas; however, there is not enough archaeological evidence to substantiate this theory. Their ancestors thought to have originated in the Mauryan period, are mentioned as small clan chiefs in medieval Sanskrit literature.
The Grand Empire of Vijayanagara
The Deccan-based Vijayanagara Empire was established in 1336 by Harihara I and his brother Bukka Raya I. It flourished until 1646 when the Deccan sultanates suffered a major military defeat in 1565. Encircling modern-day Hampi, a World Heritage Site, are the magnificent remnants of the empire named after its capital city, Vijayanagara, which is located in modern-day Karnataka, India.
Works by early European explorers such as Domingo Paes, Fernao Nuniz, and Niccolò Da Conti, as well as regional vernacular literature, contain important information about its past. Archaeological excavations at Vijayanagara have revealed the wealth and might of the empire. South India is home to several of the empire's monuments, the most well-known of which is at Hampi. The older temple construction traditions of South India were combined to create the Vijayanagara architectural style.
Because of the mingling of various faiths and vernaculars, the Vijayanagara style of temple construction was pioneering in its use of natural granite, first in the Deccan and subsequently in the Dravidian languages. Secular royal structures are examples of Northern Deccan Sultanate architecture. Strong international trade and effective government introduced new technologies, like irrigation water management systems. The arts and literature of Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, and Sanskrit reached previously unheard-of heights under the empire's patronage, and Carnatic music evolved into what it is today. In South Indian history, the Vijayanagara Empire created an era that transcended regionalism by highlighting Hinduism as a uniting force.
The city of Vijayanagara and its first dynasty were established in 1336 by five sons of Sangama; the first kings of the city were Harihara and Bukka. In due course, Vijayanagara expanded to become the biggest empire in southern India. By serving as a barrier against invasion by the Muslim sultanates in the north, it assisted in the reconstruction of Hindu life and governance following the instability and disorder of the 12th and 13th centuries. Engaging with Muslims, who were not personally disliked, sparked creative thinking and inventive products. Local literature blossomed and Sanskrit was emphasized as a uniting factor. Outside its borders, the country flourished in unmatched peace and prosperity.

Dynasties in South India: FAQs
What were the top 10 longest-ruling dynasties in India?
- Chola Dynasty
- Ahom Dynasty
- Mughal Dynasty
- Maurya Dynasty
- Shishunga Dynasty
- Rashtrakuta Dynasty
- Haryanka Dynasty
- Nanda Dynasty
- Kushans/ Yeuchi Dynasty
- Sunga Dynasty
How many dynasties were there in South India?
The major dynasties to rule South India were the Pandyas, the Cholas, and the Cheras. Other important dynasties of South India were the Pallavas, the Kadambas, the Gangas, the Chalukyas, the Rashtrakutas, the Hosalas, and the Kakatiyas.
Summarise with AI: