Science is one of the oldest and most vital academic fields, encompassing many subjects. It plays a key role in helping us understand the world around us. Everything we know about the universe, from how plants reproduce to the structure of an atom, comes from scientific research and experimentation. Scientific breakthroughs have driven human advancement throughout history. From understanding gravity to developing modern medicines, students of science have shaped the world we live in today.
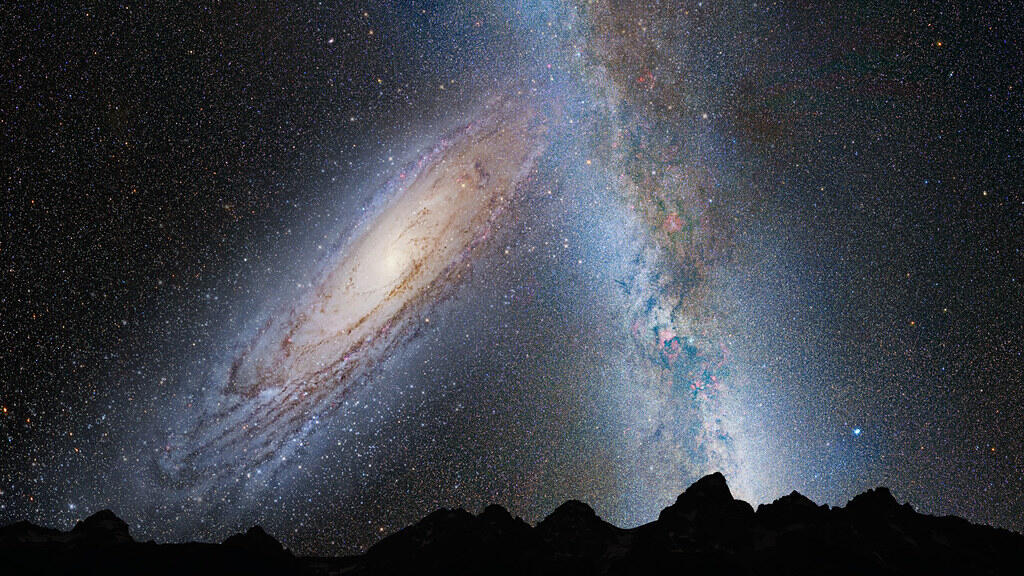
The universe encompasses everything — all of space, matter, energy, and even time. It includes you, Earth, the Moon, and the planets in our solar system, which orbit the Sun along with asteroids and comets. The Sun is just one of hundreds of billions of stars in the Milky Way galaxy, and many of these stars have their planets, called exoplanets. The Milky Way itself is only one of billions of galaxies in the observable universe, most of which are thought to contain supermassive black holes at their centers. Everything in existence, including what we can't yet observe, is part of the universe — it truly is all-encompassing.

Facts about the Milky Way
The Milky Way is our vast home galaxy, spanning over 100,000 light-years in diameter.
The Milky Way: A Barred Spiral Galaxy
The Milky Way belongs to a class of barred spiral galaxies, characterized by a central bar-shaped structure made of stars. Its spiral arms extend from the ends of this bar, and this feature is seen in about two-thirds of all spiral galaxies. The central bar influences star and gas movement, directing material toward the core and potentially contributing to star formation and the growth of the central black hole.
Vast Size and Structure
The Milky Way spans about 100,000 light-years in diameter. A light-year, the distance light travels in one year, is approximately 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers). Most of the galaxy’s stars and matter are located in a disk that is about 1,000 light-years thick, with a bulge near the center. Its sheer size encompasses countless stars, planets, nebulae, and other celestial objects.

Billions of Stars and Planets
The Milky Way contains an estimated 100 to 400 billion stars, though the exact number remains uncertain due to dust obscuring many stars. Stars range in age from newly forming in nebulae to ancient stars nearly as old as the galaxy itself. While scientists have observed around 5,000 planets (exoplanets), there may be as many as 100 to 200 billion planets within the galaxy, suggesting a wide diversity of planetary systems.
Our Solar System’s Location
Our solar system resides in a relatively quiet region of the Milky Way, located within the Orion Arm, a minor spiral arm between the larger Sagittarius and Perseus arms. We are about 27,000 light-years from the galactic center, far from the crowded and energetic core where intense radiation and densely packed stars dominate.
Galactic Orbit and the “Galactic Year”
The Sun, along with the solar system, orbits the center of the Milky Way in a journey that takes roughly 250 million years, known as a "galactic year." During this orbit, the solar system passes through different regions of the galaxy, which may influence life on Earth over extremely long timescales.
Sagittarius A*: The Central Black Hole
At the heart of the Milky Way is a supermassive black hole called Sagittarius A*, with a mass roughly 4 million times that of the Sun. This black hole plays a crucial role in the gravitational dynamics of the surrounding stars and gas, though it is relatively quiet compared to the more active black holes found in some other galaxies.
Galactic Growth and Evolution
The Milky Way continues to grow by merging with smaller galaxies, such as the ongoing merger with the Sagittarius Dwarf Galaxy. This process has contributed to its size and mass over billions of years and will continue to shape its future evolution.
The Andromeda Collision
In about 4.5 billion years, the Milky Way is expected to collide with the nearby Andromeda Galaxy. This slow but dramatic event will reshape both galaxies, eventually forming a new galaxy, sometimes referred to as "Milkomeda."
Facts about Constellations of Stars
Constellations are commonly thought of as groups of stars forming recognizable patterns in the sky, often resembling specific shapes or figures. These patterns have been named based on their appearance or cultural significance. However, while stars in a constellation may appear connected from our perspective on Earth, in reality, the stars in a constellation can be at vastly different distances from Earth.
5 Most Recognizable Constellations
| Ursa Major | Ursa Major, the largest northern constellation and third largest overall, is famous for the Big Dipper asterism. This easily recognizable star pattern has held cultural and mythological significance throughout history, featuring prominently in astronomy and folklore. Greek astronomer Ptolemy included Ursa Major in his 2nd-century star catalog, solidifying its iconic status across civilizations. |
| Ursa Minor | Ursa Minor, or "The Lesser Bear," is a constellation near the northern celestial pole, visible year-round in the Northern Hemisphere. Abbreviated as "UMi" by the International Astronomical Union, it plays a key role in astronomy and cultural lore, despite being smaller and less prominent than Ursa Major. |
| Orion | Orion, located along the celestial equator, is visible worldwide and features two of the ten brightest stars: Rigel and Betelgeuse. These, along with Bellatrix, Hatsya, Meissa, and Saiph, form the constellation’s iconic shape, resembling a hunter. Orion has been recognized and celebrated in many cultures throughout history. |
| Taurus | Taurus, the bull, is a prominent and easily recognizable constellation. It ranks as the sixth largest Zodiac constellation and covers about 1.9% of the sky. Visible in the Northern Hemisphere, Taurus is most noticeable in December and January, distinguished by its characteristic two-pronged fork of stars. |
| Gemini | Gemini, a northern zodiac constellation, was first cataloged by Ptolemy in the 2nd century. Easily identifiable by its two brightest stars, Castor and Pollux, with Pollux ranking as the 17th brightest star, Gemini also hosts the summer solstice. It is home to the intriguing pulsar Geminga, an object of great astronomical interest. |

Facts about Planets
Each planet in our solar system has unique traits, offering insights into our cosmic neighborhood.
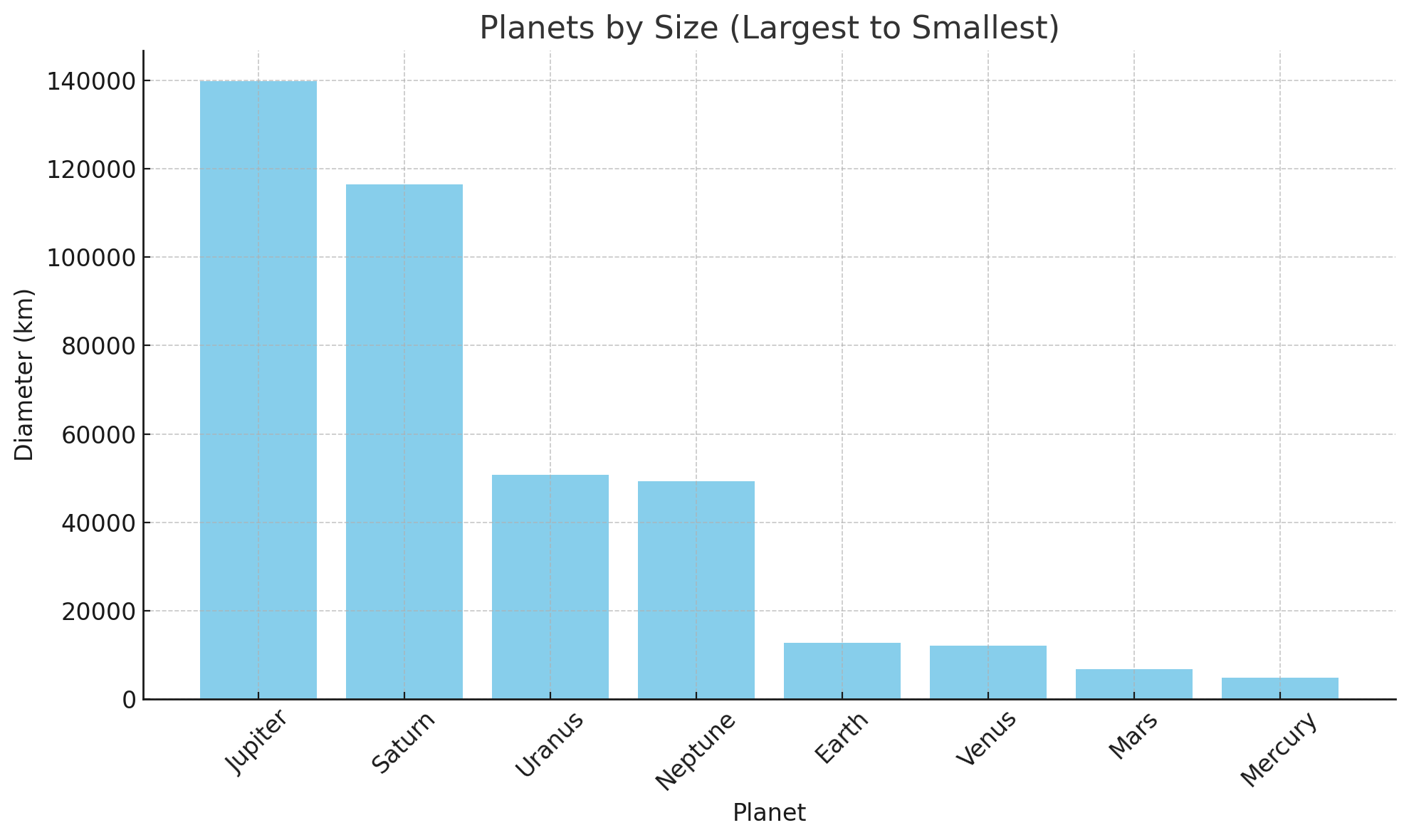
- Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun, has extreme temperature swings from 430°C by day to -180°C at night due to its lack of atmosphere. Despite its small size, Mercury's large iron core makes it the second densest planet after Earth.
- Often called Earth's twin due to its similar size, Venus is the hottest planet, with surface temperatures around 465°C (869°F). Its thick carbon dioxide atmosphere causes a runaway greenhouse effect, trapping heat. A day on Venus lasts 243 Earth days, longer than its 225-day orbit around the Sun.
- Earth, uniquely capable of supporting life, owes this to its ideal distance from the Sun, liquid water, and protective atmosphere. Its large moon stabilizes Earth’s axial tilt, moderating the climate. The planet’s biosphere, oceans, and atmosphere work together to regulate temperatures, maintaining conditions necessary for life.
- Mars, the Red Planet, features the solar system’s largest volcano, Olympus Mons, towering three times higher than Mount Everest. It’s a key candidate for future human exploration, with evidence of past water. Mars also experiences massive dust storms that can engulf the planet for weeks, affecting visibility and temperature.
- Jupiter, the largest planet, has more than twice the mass of all others combined. Its Great Red Spot, a 400-year-old storm, and 79 moons, including Ganymede, are notable features. Jupiter’s internal heat fuels its turbulent weather systems.
- Saturn is renowned for its vast, thin ring system made of ice, rock, and dust. Despite its size, Saturn is the least dense planet and would float in water. Its moon Titan, with liquid methane lakes, is also remarkable.
- Uranus rotates on its side with a 98-degree tilt, causing extreme seasons of 42 years of sunlight and darkness. It has faint rings, a cold hydrogen-helium atmosphere, and emits little heat, making it one of the coldest planets.
- Neptune, the farthest planet, has the solar system’s strongest winds, reaching over 2,000 km/h. Its blue color comes from atmospheric methane, and it hosts the Great Dark Spot storm. Neptune's largest moon, Triton, has a retrograde orbit, indicating it was likely captured.
Facts about Exoplanets
Exoplanets are planets outside our solar system, ranging from giant gas planets to rocky Earth-sized ones.
Types of Exoplanets
Exoplanets display far more diversity than the planets in our solar system, coming in various types and sizes.
- Gas giants are similar in size to Jupiter or Saturn but can be even larger. A notable type is hot Jupiters, gas giants that orbit very close to their stars, experiencing extreme temperatures.
- Neptunian planets, like Neptune or Uranus, have hydrogen- and helium-rich atmospheres and rocky cores. Smaller versions, called mini-Neptunes, exist between Earth and Neptune in size, a type absent from our solar system. Interestingly, few hot Neptunes—those near their stars—have been found, likely because stellar radiation may strip their atmospheres, turning them into super-Earths over time.
- Super-Earths are rocky planets larger than Earth but smaller than Neptune. They may or may not have atmospheres, and some could be potentially habitable.
- Terrestrial planets are Earth-sized or smaller, made mostly of rock, silicate, or carbon, and may hold atmospheres or oceans.
- Rogue planets are free-floating bodies not bound to any star. They may form within planetary systems but are later ejected or possibly form independently in space.
Exoplanets Closest to Earth Chart
| Exoplanet | Distance (Light Years) | Type | Star Type | Orbit Period (Days) |
| Proxima Centauri b | 4.24 | Super-Earth | Red Dwarf | 11.2 |
| Barnard’s Star b | 6 | Super-Earth | Red Dwarf | 233 |
| Ross 128 b | 11 | Temperate Super-Earth | Red Dwarf | 9.9 |
| Teegarden’s Star b | 12.5 | Earth-Sized | Red Dwarf | 4.9 |
| Luyten b | 12 | Super-Earth | Red Dwarf | 18.6 |
Theories about Our Universe
Space has long sparked curiosity, driving scientific exploration into the universe's nature. Astronomers, physicists, and cosmologists have developed theories to explain the universe—some supported by evidence and testing, while others remain speculative, offering intriguing possibilities for future discovery.
Big Bang Theory
The Big Bang Theory is the leading explanation for the universe's origin, proposing that it began 13.7 billion years ago from a point of immense heat and density, expanding into the vast cosmos we observe today. Although we cannot directly observe the universe’s beginnings, the "echo" of this early expansion is detectable through the cosmic microwave background (CMB), radiation that permeates space. This afterglow, first predicted in 1948 and discovered two decades later, provides vital evidence for the Big Bang.
In its early stages, the universe was a dense plasma of fundamental particles that scattered light, much like sunlight scatters in clouds. Roughly 380,000 years after the Big Bang, these particles formed neutral atoms, allowing light to pass freely, creating the CMB.
Dark Matter and Dark Energy
Dark matter, which constitutes about 27% of the universe, does not emit or absorb light and is only detectable through its gravitational influence on visible matter. In contrast, dark energy, making up around 68% of the universe, is linked to the vacuum of space and drives the accelerated expansion of the universe. Together, dark matter and dark energy shape our understanding of the cosmos, yet remain mysterious forces.

Holographic Principle
The Holographic Principle suggests that all information in a region of space can be described by a theory on its boundary. For instance, everything happening inside a room could be fully explained by a theory operating on the room's walls. The principle also asserts that this boundary theory contains no more than one degree of freedom per Planck area—a fundamental unit of space derived from universal constants and extremely small, measuring approximately 1.6 x 10^-33 cm.
Cosmic Inflation Theory
Around 13.8 billion years ago, the universe underwent a rapid, faster-than-light expansion known as cosmic inflation. This brief but intense expansion occurred in less than a second, though its cause and what preceded it remain uncertain. Some theories suggest that inflation was driven by a fundamental property of space-time.
Cosmological Principle
The cosmological principle asserts that the universe is homogeneous (consistent in composition) and isotropic (appears the same in all directions) on large scales. This principle implies that the universe has no preferred center or edge, and the laws of physics apply uniformly across all regions.
Unlocking the Universe's Mysteries
Science offers endless opportunities for discovery, sparking curiosity about our expanding universe. From exploring planets in our solar system to studying distant exoplanets and theorizing about the universe's origins, students of science are shaping the future. As our knowledge expands, we continue to unlock new secrets, revealing the wonders of space and deepening our understanding of our cosmic neighborhood.
Summarise with AI: