Mathematics shapes everyday life in ways we often don’t notice—from managing money and planning schedules to powering technology, transport, and communication. It helps us understand patterns, make informed decisions, and solve real-world problems with clarity and logic.
Why maths is important in the modern world:
- Improves problem-solving skills by teaching logical and structured thinking.
- Supports financial decisions, from budgeting to investing.
- Enables technological progress, forming the basis of coding, AI, and engineering.
- Helps interpret data, a key skill in almost every profession today.
- Strengthens analytical thinking, crucial for science, business, and research.
- Makes daily tasks easier, like measuring, planning, or comparing options.
- Builds critical reasoning, helping people evaluate information and avoid errors.
- Enhances career opportunities in STEM fields and beyond.
Have you ever considered just how much of an influence Maths has on our everyday lives?
No, we're not talking about fractions or completing worksheets but maths in the form of logic and problem-solving crop up constantly outside of the classroom. Mathematics is more a part of our everyday lives than many would think and allows us to better understand the world around us.
The use of numbers and figures can be found everywhere, from cooking to medicine to the media with their percentages and graphs. Here we'll shed light on several areas where maths is centre stage.
Our understanding of math and the constant desire to know more about everything in this world so that, today, the world as we know it would not be possible without maths.
Mathematics is an application of matter and contributes to all of our methodical and systematic behaviours.
It is Maths, for instance, that has brought order to the communities across this planet and prevented chaos and catastrophes. Many of our inherited human qualities are nurtured and developed by Maths theories, like our spatial awareness, our problem-solving skills, our power to reason (which involves calculated thinking) and even our creativity and communication.
If you are looking for an online maths tutor then you must try Superprof. Superprof has more than 100,000 teachers from all over India taking private tuition for all school boards whether CBSE or HSC.

Brief History Of Maths
The history of mathematics explores the beginnings of mathematical discoveries, as well as the mathematical techniques and symbols used in the past. Before the modern era and the global dissemination of knowledge, written evidence of new mathematical advancements was limited to a small number of locations.
Around 3000 BC, the Mesopotamian civilizations of Sumer, Akkad, and Assyria, along with Ancient Egypt and the Levantine state of Ebla, started employing arithmetic, algebra, and geometry for purposes such as taxation, commerce, trade, and astronomy, including timekeeping and calendar creation.
Since maths is a broad application of matter, rather than a discovery, we cannot credit one person with the invention of maths itself, however, we can take a look back at when maths started to play a role in the life of humans.
Unsurprisingly, evidence shows that this was pretty much the beginning of time as we know it! Even those living in prehistoric times had some understanding of maths concepts, records of which were found on many items, like bones, and wall carvings.
Markings would have shown that they used rational thinking when learning how to solve simple math problems like adding things up on a surface area.
Get help with your coursework when you find maths tutors near me on Superprof.
Early Mathematical Developments
The earliest mathematical subjects were arithmetic and geometry, with applications in accounting and architecture. These emerged in ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Greece.
Medieval and Renaissance Advancements
During the Middle Ages and Renaissance, mathematicians made significant contributions in algebra, trigonometry, and calculus. This period also saw the development of the Arabic numeral system and the printing press, which facilitated the spread of mathematical knowledge.
Modern Breakthroughs
The 19th and 20th centuries witnessed groundbreaking discoveries in mathematics, including non-Euclidean geometry, set theory, and the theory of relativity. The development of computers further revolutionized the field, enabling complex calculations and simulations.
What Is The Fear Of Mathematics Called?
Numerophobia The fear of mathematics is called numerophobia, also known as arithmophobia or mathematics anxiety. It is an anxiety disorder characterized by an intense fear of dealing with numbers or mathematical concepts.
Numerophobia can manifest in various ways, including feelings of panic, anxiety, and avoidance of situations involving math. It can be triggered by specific mathematical tasks, such as solving equations, or by broader concepts like statistics or geometry
Renowned Indian scholars, including Dr. Anuradha Saha and Dr. Sanjay Kumar, have conducted research revealing the high prevalence of math phobia among Indian students.
The study published in the Journal of Indian Education found that nearly 60% of surveyed students experienced math anxiety, with girls showing higher vulnerability than boys.
Saha & Kumar, 2018
This underscores the importance of implementing specific interventions to tackle this problem.
Students may find math challenging for seDveral reasons, and while it's not universally a "nightmare," there are common factors that contribute to math anxiety and difficulty. Here are some reasons why students may find math challenging:
Complex Concepts: Mathematics often involves abstract and complex concepts that can be difficult to grasp. For some students, these concepts may seem intimidating or overwhelming.
Lack of Understanding: If a student falls behind in understanding foundational math concepts, it can create a snowball effect, making it even harder to comprehend more advanced topics.
Fear of Making Mistakes: Many students fear making mistakes in math, as they believe there's no room for error. This fear of failure can lead to anxiety and hinder learning.
Ineffective Teaching Methods: Inadequate teaching methods or a lack of engaging instruction can make math less enjoyable and harder to learn.
Negative Mindset: Negative beliefs and attitudes about math can influence a student's perception of the subject. Statements like "I'm not a math person" can become self-fulfilling prophecies.
Math Anxiety: Math anxiety is a real psychological phenomenon that can cause physical and emotional distress when faced with math-related tasks or tests.
Limited Practice: Math is a skill that often requires consistent practice. Students who don't practice regularly may struggle to retain and apply mathematical concepts.
Lack of Real-World Application: Some students find it challenging to see the real-world relevance of math concepts, which can make it seem abstract and disconnected from their lives.
Peer Pressure: Peer pressure and social stigma can play a role. Students may be teased or labeled as "nerdy" for excelling in math, which can discourage some from pursuing the subject.
Inadequate Support: Students who lack access to resources like tutors or additional help outside of school may struggle to overcome math difficulties.
Find support when you search for maths tutors near me on Superprof.
Dyscalculia or Numerophobia
Dyscalculia: A learning disability characterized by difficulty understanding and manipulating numbers. It is a neurological condition that affects a person's ability to learn and process mathematical concepts.
Numerophobia: An extreme or irrational fear of numbers. It is a type of phobia that can cause significant anxiety and distress in individuals who experience it.
Understanding Dyscalculia Symptoms:
- Difficulty understanding and manipulating numbers
- Problems with basic arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division
- Struggling to grasp mathematical concepts and problem-solving
- Difficulty with time management and telling time
- Challenges with estimating quantities
- Trouble with spatial awareness and understanding directions
- Difficulty remembering math facts and formulas
- Anxiety or frustration towards math-related tasks
Understanding Numerophobia Symptoms:
- Extreme fear, anxiety, or panic when dealing with numbers
- Avoidance of any situations involving numbers, math, or numerical information
- Physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling when exposed to numbers
- Feelings of helplessness, dread, or terror when faced with numerical tasks
- Difficulty concentrating on numeric-based activities
- Worrying excessively about making mistakes with numbers
- Disruption to daily life and activities due to the fear of numbers
- Recognizing the fear is irrational but still being unable to control it
The key difference is that dyscalculia is a neurological learning disorder, while numerophobia is an irrational fear or phobia of numbers and math. The symptoms reflect the underlying condition in each case.
Why Maths is Important?
Mathematics is important for a variety of reasons, and its significance extends across many aspects of life, including education, science, technology, business, and everyday problem-solving. Here are some key reasons why math is important:
- Foundation of Learning: Mathematics serves as a fundamental building block for learning in various subjects, including science, engineering, economics, and computer science. It helps develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Problem Solving: Math equips individuals with the ability to analyze and solve complex problems, both in academic and real-life situations. It encourages logical thinking and structured reasoning.
- Career Opportunities: Many careers and professions require a strong mathematical foundation. Engineers, scientists, architects, financial analysts, data scientists, and computer programmers, among others, rely heavily on mathematical concepts and tools.
- Technological Advancements: Mathematics is at the core of technological advancements. It plays a crucial role in the development of computer algorithms, software, artificial intelligence, and various technologies that shape our modern world.
- Scientific Research: Mathematics provides the language and tools for scientists to model, analyze, and understand natural phenomena. It's essential for disciplines like physics, chemistry, biology, and astronomy.
- Economic Decision-Making: Economics relies on mathematical models and statistical analysis to make informed decisions about resource allocation, investments, and policy development.
- Financial Literacy: Understanding math is crucial for managing personal finances, including budgeting, saving, investing, and understanding loans and mortgages.
- Data Analysis: With the increasing importance of data in various fields, statistical and mathematical skills are essential for interpreting and making informed decisions based on data.
- Innovation and Invention: Many inventions and innovations are the result of mathematical insights and principles. Math drives advancements in fields like medicine, transportation, and communication.
- Everyday Life: Math is a part of our daily lives, from calculating expenses, cooking, measuring ingredients, and making informed choices as consumers.
Need help with your maths classes? Find maths tutors near me on Superprof!
Aryabhatta is known as the pioneer of Indian mathematics. His significant contributions include advancements in spherical trigonometry, plane trigonometry, and the accurate calculation of the value of π up to four decimal places.
A lot of teachers in India teach mathematics with the help of formulas that are derived from Vedic maths. A Superprof Maths tutor can ensure you learn this subject without any issues. We use math in countless ways every day, from simple tasks like measuring ingredients while cooking to complex calculations involved in engineering and technology.
Budgeting, tracking expenses, calculating interest rates, and making informed investment decisions all rely heavily on math skills. Math helps us understand and navigate the world around us, from reading maps and blueprints to estimating distances and sizes.
To learn maths is to open up a world of opportunity - now you see the importance of maths tutors and the impact they can have on your life!

Important Maths Facts That We See Everyday
- Addition and subtraction: We use addition and subtraction when we balance our checkbook, calculate our change when making a purchase, or figure out the total cost of our grocery bill.
- Multiplication: We use multiplication when we calculate the total cost of multiple items at the grocery store, figure out how many hours we worked at our job, or determine how much to tip a server based on a percentage of the total bill.
- Division: We use division when we split a bill with friends, calculate the cost per unit of a product, or figure out how much we need to save each month to reach a financial goal.
- Fractions and decimals: We use fractions and decimals when measuring ingredients for recipes, calculating percentages for sales and discounts, or determining the amount of time we need to complete a task.
- Geometry: We use geometry when we plan our garden, arrange furniture in a room, or calculate the area and perimeter of a space.
- Time and distance: We use time and distance calculations when we plan our commute, estimate how long it will take to complete a task, or determine the best route for a road trip.
What Careers Are Based on Mathematics?
If you still doubt the ubiquitous and essential role of mathematics in the professional world (and thus in our daily lives), be prepared to have your perspective changed.
This science, inherited from antiquity, constitutes a common foundation for many professions.
Whether one works in formulating medicines, meteorology, designing medical imaging devices, using statistics, managing personal data with cryptography, or in the more abstract world of pure maths, the same language is used.
Arithmetic, algebra, complex numbers and probability are all elements of the grand discipline that is mathematics; one that shapes our everyday lives.
For example, astronomers searching for life on other planets, statisticians using maths revision to study population fluxes and accountants measuring trade balances of firms and countries: All share a common ground, studied during their mathematics education and honed with experience.
Whilst Maths opens up a variety of exciting and varied doors career-wise, the most common jobs for Maths graduates, however, are:
- accountant
- actuary
- investment manager
- investment banker
- retail banker
- statistician
- data analyst
- data scientist
- researcher (maths)
- teacher (maths)
- meteorologist
- computer engineer
If you're seeking a career in Finance, then some level of math qualification is required, but you may not necessarily need a degree.
Aside from the financial sector, there are industries such as engineering and information technology that can benefit from someone who is good with numbers.
For example, roles like defense and intelligence officer, statistician, operational researcher, academic mathematician, teacher of Maths in a primary or secondary school, or positions within the law, media, business or public sectors.
Some of your typical employers might be the government, educational establishments, IT companies, pharmaceutics companies, engineering companies, insurance companies, marketing or market research companies, and banking and accountancy firms.
Importance Of Maths In Sports
- Statistics: Statistics are essential in sports. Coaches and analysts use statistical data to evaluate player performance, identify strengths and weaknesses, and develop training plans. For example, batting averages and on-base percentages are used in baseball to evaluate the performance of batters. Similarly, shooting percentages and assists per game are used in basketball to evaluate the performance of players.
- Game Theory: Game theory is a branch of mathematics that is used to analyze strategic decision-making. In sports, game theory is used to determine the best strategies for teams to win games. For example, in soccer, teams may use game theory to decide whether to play an offensive or defensive game, based on the strengths and weaknesses of their opponents.
- Trajectory and Motion: Mathematics is also used to analyze the trajectory and motion of objects in sports. For example, in football, math is used to calculate the trajectory of a ball during a field goal attempt. Similarly, in baseball, math is used to calculate the trajectory of a pitched ball and to analyze the motion of a thrown ball.
- Equipment Design: Mathematics is used in the design of sports equipment. For example, the design of golf clubs and tennis rackets is based on mathematical principles.
Why Is Maths Important In Professions?
Below is a recap of just some of the industries and related posts that you could be working in if you pursue Maths as a subject to a high degree.
| Sector | Role |
|---|---|
| Financial | Accountant, Actuary, Banker, Analyst, Statistician |
| Engineering | Computer engineer, Mechanic |
| Science | Researcher, Statistician, Meteorologist |
| IT | Computer engineer, Designer |
| Medical | Doctor, Nurse |
Mathematics and the Study of the World
From the study of our solar system to the reproductive cycle of animals and the growth of plants, mathematics is very useful in understanding the world around us.
And yes, maths can even be used to solve puzzles!

Not all calculations are necessarily complicated: We can use complex functions or sequences as readily as simple methods, for example to mark and follow individuals in the study of populations and evolution.
Engineers test materials in order to design durable and safe structures, using calculations of the strength and density of materials.
In cartography, it's necessary to accurately measure angles and draw distances that will allow locations to be precisely represented. Such knowledge is used not only by the surveyor, but also by the treasure hunter looking for sunken wrecks, using instruments derived from a compass.
The price of food is calculated in relation to production and estimated demand. The predicted course of a pandemic is determined by studying the pathogen's rate of transmission. It's even useful for doing homework or revising for a maths exam! The list of uses is endless.
If you want to progress in math, don't delay in signing up for maths tuition with a maths tutor.
In short, everything comes under the influence of maths, even the world of professional-level sport!
Even when it comes to the esoteric, maths has left its mark. Many mathematicians have sought hidden meaning in numbers, and predictive properties with numerology, not to mention the mysterious golden ratio found in nature as well as in extraordinary human constructions, like the pyramids.
There are also many maths equations that have changed the world!
Whoever said that maths was irrelevant in daily life?
And as an added bonus, maths is a great way to play the odds in poker and come out the winner!
Use of Mathematics in Health
Human life in its earliest developmental stage can be seen in-utero using ultrasound: When the fœtus is only slightly bigger than a bean, it can be visualised, and its heartbeat heard. Mathematics then comes into play in a child's health record, showing their estimated growth curve in relation to weight and height.
Medical imaging can be used to determine any fractures with an x-ray, developed using maths, or an MRI scan, which exists thanks to calculus.
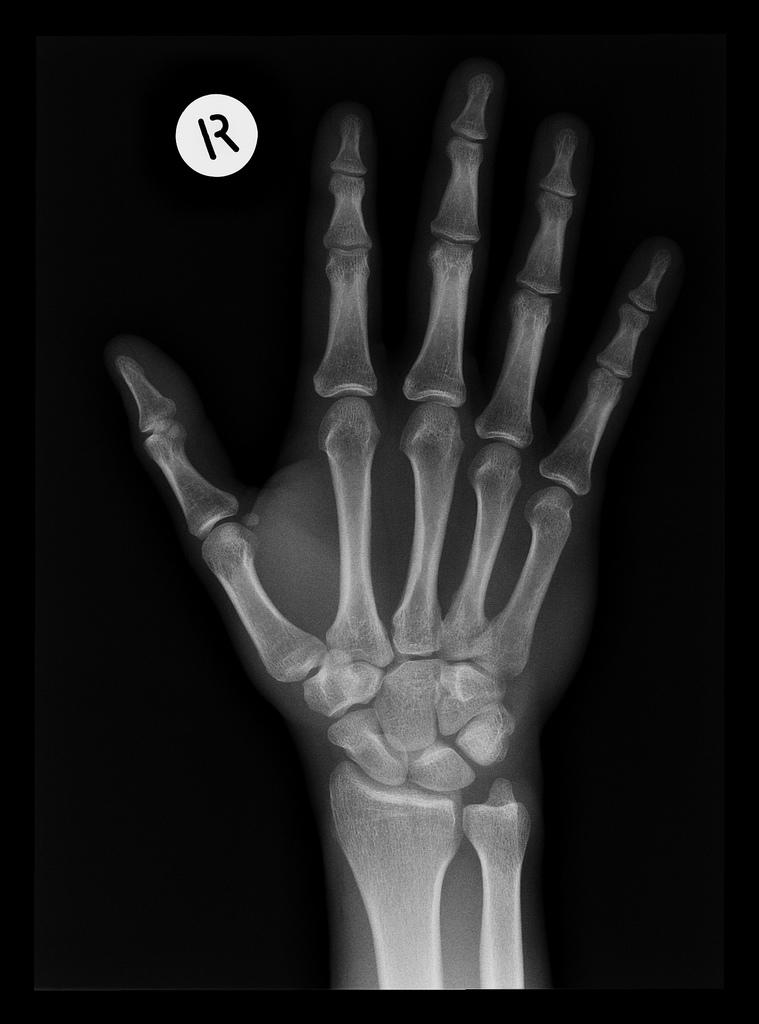
This practical application of maths is used in oncology, to understand cell mutation and develop curative treatments that help save many lives.
In an effort to combat illness and injury, statisticians analyze the results of studies carried out using volunteers, in order to identify models for advancing research on new drugs.
Looking to find out whether your body mass index (BMI) is within the normal range?
All you have to do is perform the following simple calculation: BMI = Weight(kg) / Height(m)^2. Results in the normal range should be between 18.5 and 25.
Human beings have, with access to a growing body of knowledge, wrought great changes in the natural world. We have created new diseases that we must now attempt to cure, and caused widespread pollution, which we must now seek solutions in order to fight.
Through these few examples, we can see the extent of mathematics in our daily life, on individual, societal, planetary and galactic scales.
Isn't it fascinating, to see how the infinitely small can help us understand the infinitely great?
Don't wait any longer, get stuck into maths right now! Find a tutor for CBSE maths revision or, more specifically, search for online maths tutors near me.
Summarise with AI:
















Better work