Division is one of the four basic mathematical operations, the other three being addition, subtraction, and multiplication. In simple words, division can be defined as splitting a large group into smaller groups so that every group will have an equal number of items. It is an operation used for equal grouping and equal sharing in math.
Division skills are a staple of elementary math. Students' number sense and logical skills by learning to divide are key to advancing their math skills. Like any STEM subject, math concepts, including division, build upon each other like rungs of a ladder.

All About Division
Division is denoted by a mathematical symbol that consists of a small horizontal line with a dot each above and below the line. There are two basic division symbols that represent the division of two numbers. They are ÷ and /.

Parts of Division
Parts of division mean the names of the terms associated with the division process. There are four parts of division, which are dividend, divisor, quotient, and remainder.
- Dividend: The dividend is the number that is being divided in the division process.
- Divisor: The number by which the dividend is divided is called the divisor.
- Quotient: The quotient is a result obtained in the division process.
- Remainder: Sometimes, we cannot divide things exactly. There may be a leftover number. That leftover number is called the remainder.
Find out the best ways to learn maths in India.
The relationship between these four parts can be expressed as follows:
Dividend = Divisor x Quotient + Remainder
This is also called the division formula to check whether the answer is correct or not.
Properties of Division
- Division by 1: Any number divided by 1 results in the number itself. In other words, if divisor = 1, then dividend = quotient.
- Division by 0: The value of a number divided by 0 is not defined, i.e., n/0 = not defined, where n is any number.
- Division by itself: If we divide a number by itself, we will always get 1 as the answer. In other words, if dividend = divisor, then quotient = 1.
- Division of 0 by any number: 0 divided by any number always results in 0. Some examples are 0 ÷ 4 = 0, 0 ÷ 9 = 0, 0 ÷ 5754 = 0, etc.
- Division by 10: If we divide a number by 10, then the digit in the ones place will always be the remainder, and the remaining digits on the left will be the quotient. For example, 579 ÷ 10 = 57 R 9.
- Division by 100: If we divide a number by 100, the number formed from the ones place and the tens place digits will always be the remainder. The remaining digits on the left will be the quotient. For example, 8709 ÷ 100 = 87 R 9.
Learn Division Fast and Easy
In maths for beginners, it may seem difficult to understand division. However, Superprof offers a few simple trade tricks to make your learning smooth! Once mastered, these division tricks will make basic math a breeze! Whether you need help with quick calculations or are memorizing your math facts, it comes in handy to have one or two “math hacks” ready to go!
Find out the best ways to learn multiplication.
Dividing by 1
Any number divided by 1 is the number itself! For instance, 300 divided by 1 is 300.
Dividing by 2
Every even number is divisible by 2; that is, any number ending in a 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8. For instance, 566 can be evenly divided by 2: 283.
Dividing by 3
Here’s a lesser-known fun fact: if the sum (the total of numbers added together) in a given number can be divided by three, so can the number! For example, the number is 21. 2+1 = 3. 21 divided by 3 = 7.
Dividing by 4
When dividing by 4, look at the last two digits of the number. Are those two digits divisible by 4? That means the entire number is also divisible by 4!
Dividing by 5
Any number that ends in a 0 or a 5 is always divisible by 5. Like 10 is divisible by 5, so is 82984780 (the quotient is 16,596,956).
A mathematics teacher can help you master any maths concept.
Dividing by 6
This division hack has two steps, but it’s worth the practice. If the above rules for 2 and 3 are true, then you can divide the number by 6 as well. For instance, if a number’s digits add up to something divisible by 3 and end in an even number, it will be divisible by 2, 3, and 6. 960 divided by 3 is 320.
Dividing by 7
This one is a little trickier and works with three digits or longer numbers. To check if the number is divisible by 7, start with the last digit of the number. Double that number, then subtract the doubled number from the remaining two digits of the number.
Example: Let’s say the number is 161. First, double the 1 to get 2. If you subtract 2 from 16, you get 14, which is divisible by 7. Therefore, we can say that 161 is divisible by 7. And when we check out work, sure enough, 161 divided by 7 is 23!
Dividing by 8
This is another division hack that works with larger numbers. If the last three digits create a number that is divisible by 8, the entire number will also be divisible by 8. For example, in 9180, the last three digits - as their own number - can be divided by 8, as can 9128. 9128 divided by 8 is 1,141!
Dividing by 9
If the sum of all of the digits of the number is divisible by 9, then the number itself is divisible by 9. For instance, the sum of the number 72 is 9, and when it’s divided by 9, the answer is 8!
Find out the best ways to learn fractions.
Dividing by 10
Similar to the trick of dividing by 5, if a number ends in a 0, it’s divisible by 10. As a bonus, the answer dividers are looking for will exist in the number already in the hundreds, tens, and ones place. For instance, 250 divided by 10 is 25.
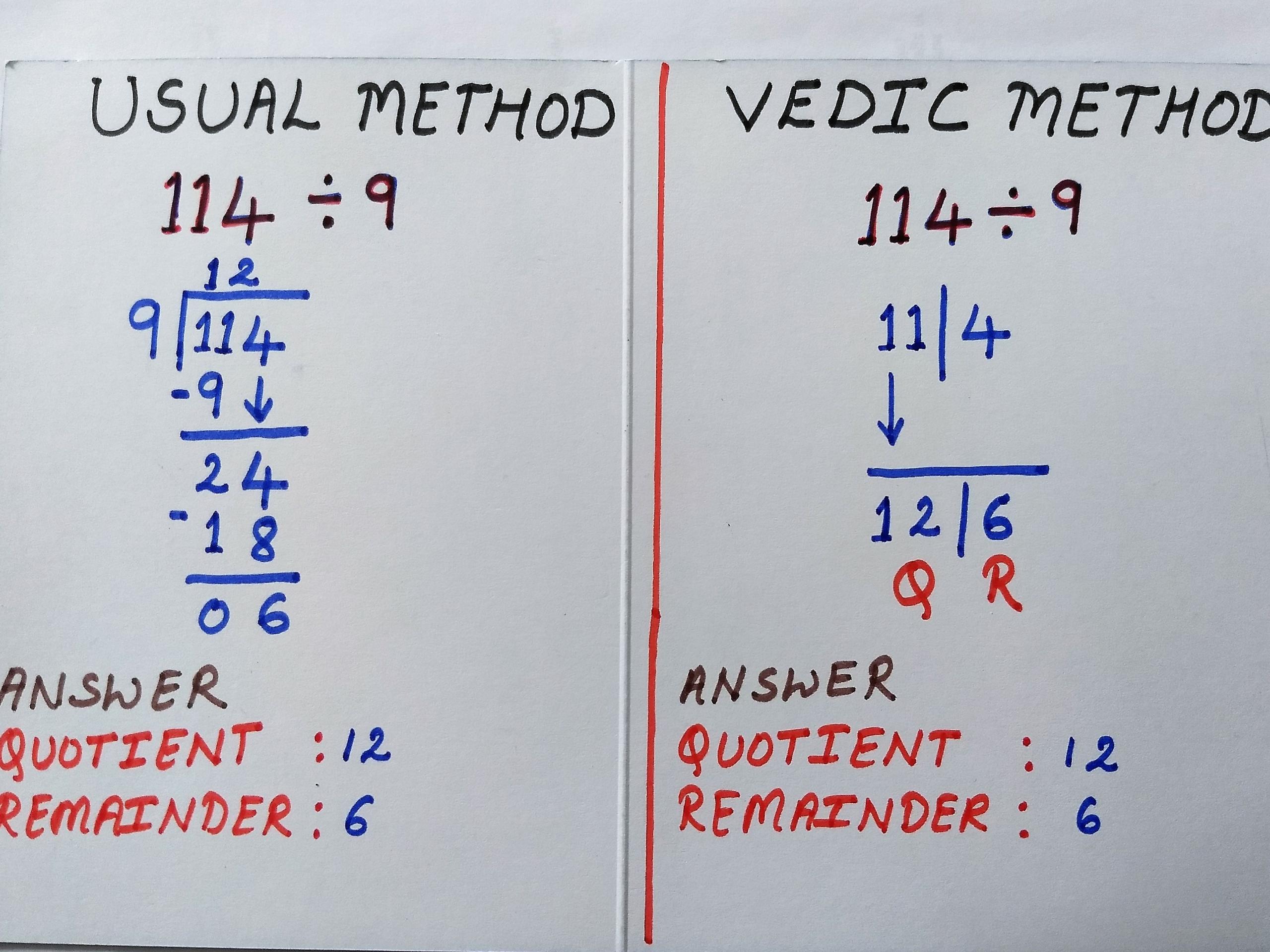
Vedic Maths Tricks for Quicker Division
Vedic Mathematics is a collection of formulae/techniques called sutras that help us solve arithmetic problems. The techniques are said to have been derived from multiple Sanskrit texts. The Sutras in Vedic Mathematics were put together by the Indian mathematician Bharati Krishna Tirthaji around the early 20th century. Let us learn a few division tricks as explained in Vedic Math Sutras.
When the divisor is smaller and closer to the power of 10 (Nikhilam)
- Identify how much short the divisor is to the power of 10.
- Split the dividend into 2 parts – Quotient and Remainder. The number of digits considered as the remainder is the same as the number of digits in the divisor.
- Multiply the first digit of the quotient with the number obtained from step 1. Add this to the unit’s digit of the quotient part (from step 2).
- Multiply the number obtained from step 3 with the number from step 1. Add this number to the Remainder part (from step 2).
- Now, we check if the remainder is greater than or equal to the divisor. If yes, divide it again and add the new quotient part to the quotient (from step 2). The remainder obtained now is the final remainder.
Having trouble understanding maths? You can find an online maths tutor today.
When the divisor is greater and closer to the power of 10 (Paravartya Sutra)
- Discard the first digit of the divisor and transpose the remaining digits of the divisor.
- Split dividend into 2 parts – Quotient and Remainder. The remainder should have the same number of digits as obtained in step 1.
- Follow the same steps as Nikhilam.
Make learning fun and efficient with the best maths revision aids.
When the divisor does not come under the rules of Nikhilam or Paravartya Sutras
(Anurupyena Sutra)
- To convert the divisor so that the Nikhilam method can be used, we multiply it by a factor which makes it closer to a power of 10
- Follow the same steps as Nikhilam.
- Once the quotient and Remainder are obtained, multiply the quotient by the same factor used in step 1.
- Check if the remainder is bigger than or equal to the divisor and take appropriate action as explained in the Nikhilam method.
Of all the math operations, multiplication and division may be the hardest for kids to learn. Tackling these skills is the logical next step after addition and subtraction. Division is typically the hardest math concept for kids to learn. Learning to divide starts in third grade. Kids are introduced to the concept by doing repeated subtraction. It’s not uncommon for kids to struggle with division. There are many reasons for that and many ways to help. Supports like separate instruction or learning in a smaller group can make a big difference over time. For all those struggling with this core maths concept, check out Superprof maths tutors who can help you befriend division!
Summarise with AI:















